Example IX |
Write an algorithm and flow diagram for adding natural numbers. Natural numbers are positive integers in the set {1, 2, 3, ... infinity}. The set of natural numbers in mathematics is denoted by the capital letter N. The set is often extended by the zero number, in which case it is denoted by N0. The limit value up to which the computer can be added depends on the capabilities of the processor and the software for programming.
Algorithm:
start ----------------------------------------------------- X=0 SUM = 0 Input N X = X + 1 SUM = SUM + X If X < N Then go back to 'X = X + 1' Print SUM ----------------------------------------------------- end
| Flowchart: | Program code: |
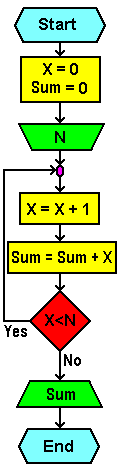 |
--------------------------------------
10 CLS
20 CLEAR
30 X = 0: sum = 0
40 INPUT "Input aggregate limit:" N
DO
X = X + 1
sum = sum + X
LOOP WHILE X < N
REM Using 'LOOP UNTIL' at first
REM complied the condition
REM goes out of the loop
50 PRINT "Sum is:" sum
60 END
--------------------------------------
10 CLS
20 CLEAR
30 x = 0: sum = 0
40 INPUT "Input aggregate limit:" N
FOR i = 1 TO N STEP 1
x = x + 1
sum = sum + x
NEXT i
50 PRINT "Sum is:" sum
60 END
--------------------------------------
|
Write an algorithm and flowchart that loads N integers. Calculate the sum of all positive and the sum of all negative numbers.
Algorithm:
start ----------------------------------------------------- Input N number = 0 positive = 0 negative = 0 Input X If X > 0 Then positive = positive + X Else negative = negative + x number = number + 1 If number < N Then go back to 'Input X' Print positive, negative ----------------------------------------------------- end
| Flowchart: | Program code: |
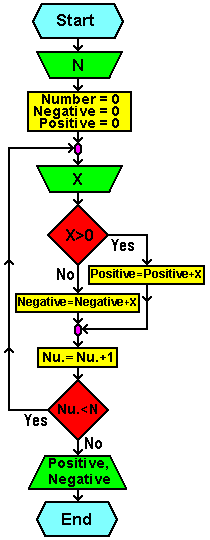 |
10 CLS
20 CLEAR
30 number = 0
40 positive = 0
50 negative = 0
60 INPUT "Input aggregate limit:" N
DO
INPUT "Input larger of limit:" X
IF X > 0 THEN
positive = positive + X
ELSE
negative = negative + X
END IF
number = number + 1
LOOP WHILE X < N
REM Using 'LOOP UNTIL' at first
REM complied the condition
REM goes out of the loop
70 PRINT "Sum of positive:" positive
80 PRINT "Sum of negative:" negative
90 END
|
The listed ten examples were written with the programming tool that has not been 'live' for a long time, but is easy to understand. If by any chance the traffic of these pages increases, this may be a motive to expand these pages with the contents of some other programming tool. The algorithm and flowchart are the same, but the implementation and selection of programming tools depends primarily on the type of device and OS, and there are quite a few newer tools for programming.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |