A widely used standard for connecting disk (and other) devices on a separate bus is SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) standard. The joint connecting cable connects to multiple devices, each of which has a different address and that are related to connecting water controller - adapter (controller) inserted in a slot connected to the computer bus. In the version of SCSI-1 and SCSI-2 (no longer used) can connect up to eight devices, and SCSI-3 version of the device four p.m., with a transfer rate of 40 Mb/s to 5 Gb/s depending on the revision of the interface. The controller is a separate and distinct unit typically has an external connector and allows connection of devices outside the computer chassis as printers, scanners and the like. The system is faster, but more expensive. Is supported by nearly all computing platforms. Controller has its own BIOS that can be adjusted so the computer's BIOS and in some ways is an extension of your computer's BIOS. Of course it is a complete hardware solution, which is better than the cheaper devices that rely to the drivers and the operating system.
Every device connected to the SCSI series is characterized by logical identifier, which is addressed by the system. This label is known as the SCSI ID is determined at the time the device is connected to the system and must be unique. Mostly defined switches on the device, although newer drives your id furniture automatically. And controller is also SCSI device, and it has an identification number, usually the number 7, is often fixed. Electronics of these devices is more complex than PATA and SATA system and is significantly more expensive. Besides, the devices are manufactured to withstand the loads and long lasting discs revolve almost twice the speed compared to SATA drives. PATA disk system identification is performed jumper (jumper) which, in principle asks the 'M' (master) or 'S' (slave) marked position. For one control over the connecting cable can be controlled by two disk devices have the same IRQ, but over the jumper specifies different identifiers (device '0' and '1'). It should take into account that both drive on the same cable same options regarding transfer rates. With SATA controller system identifier assigned to each channel and the associated port to which it can be connected to only one disk (no jumper on the drive.)
SCSI system that allows one device to connect to two (or more) computers simultaneously. This is not illogical because the machine does not know that the computer is connected, but only executes the commands it receives over the highway. Property SCSI system connectivity to devices not being treated through physical attributes, but through logical. If you use two controllers in two computers and one drive is no reason not to do so, provided that all other requirements are met as specified. SCSI Device Manager tab in the computer usually has a connector (interface) for external peripherals on a tin facade cards, and some of the particular problems in connecting no. Stated one of the prerequisites to create CLUSTER, interconnected computers in order to increase resource utilization and total computing power.
The cable that connects the device length of 10 cm to 25 m, depending on the technology of cable and cable ways reasoning. Passive inference is simply a 'resistant' conclusion at the end of the cable where the resistance value corresponds to the cable impedance, and actively supervised inference impedance cables at the end of the chain, and adapts to her and therefore more possible cable length. All previous-generation SCSI interfaces are designed on the principle of parallel data transfer. Technology is a logical successor to the serial communications SAS (Serial Attached SCSI). Apart from changing the interfaces and modes of communication, the higher the data rate (v3.0 - 12 Gb/s), provides far but the number of devices (16'256) in one domain, compatibility with the preceding standards, and has the ability to work with concerted SATA disks. SAS and SATA compatibility (using the same physical connectors) allows the user the flexibility to choose the devices that will be used, which is of great importance for the development of both standards and their application in a diverse range of computer systems, from home computers to data storage systems such as a network for connecting computers into a single data repository Storage Area Network - SAN and Network Attached Storage - NAS. The difference is in the way the operating system sees disks store. SAN operating system are presented as one large drive and are usually more complex and larger devices that can have a large number of internal disks. NAS has its own operating system that controls internal disks and provides users controlled the resources at our disposal. Operating systems and NAS may not be concurrent but must have adequate software to support each other 'understanding'.
SCSI devices are professional devices and are not subject alphabet. But what is important to mention is the support for RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) system, the ability to be more physical disks can be linked into a single logical unit (volume) in order to increase performance and resistance to failure. Server without connecting disks RAID systems is unreliable. Modern motherboards for home and semi-professional use enabling RAID with PATA and SATA disks.
RAID
In early 80-ies of the capacity of hard drives has been limited and disks with large capacity were rare and expensive. Thus began experimenting with arrays of smaller, cheaper hard drives. Researchers at Berkeley (USA - California) presented the basic rules for disk arrays. They introduced the term RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks) to emphasize the benefits of properly implemented disk arrays can provide. Presented guidelines for the development of six different models of disk arrays, RAID 0 to RAID 6. Number does not indicate a hierarchy so that does not mean that the RAID 6 are better or worse than a RAID 0 disk array. As technology has advanced hard disk drives and the cost per megabyte is falling in, the term ' Inexpensive' has been redefined 'Independent' to highlight the advantages of a disk array. RAID disk arrays has become an inevitable part of the server. Acceptance of RAID technology have resulted in the four most important facts:
- The need for greater capacity - increase the size of the application seeks a larger disk space (volume). RAID disk array provides high storage capacity and good opportunities to expand.
- Faster microprocessors - the development of microprocessors is much faster than the development of hard drives, which led to the great disparity in the speed of the data. Properly implemented RAID system can reduce the huge difference compared to a hard disk.
- Reliability - how time-critical applications moved to the server, RAID array hard drives have become a means of ensuring continuous access to data and to avoid loss of information in the event of hard disk failure. RAID systems incorporate redundancy and recovery of data in case of hard drive failure in the system.
- Price - reducing cost RAID technology began to spread with large systems on network servers, workstations and home computers.
Characteristics and principles of operation of some methods for creating disk array are:
- JBOD or SPAN (Just a Bunch Of Disks - Concatenation) - In literature often called 'LINEAR'. A popular way of connecting content over different physical disks in the 'single logical disk'. Disks can be completely physically distinguished by characteristics. Some RAID devices make it possible to see each of the disks as a single disk that can be added or subtracted group drives. If all disks merged into one, the data files are written to the blocks that do not have to follow the order of drives, that is, after the example of the sequence of records in the first five blocks of the first disc, than can follow the records into blocks in the same or the next disc and continue the above analogy. Data that is included on the new disc are instantly available without agreeing sequence blocks. The total capacity of the field (volume) is equal to the sum of the individual capacities of all the drives in the field. The system does not tolerate failure of any disk.
- RAID 0 (striping) - data. Data written to one file at the same time on all drives and hence follows the high speed data access. All drives in the field are displayed as a single volume which holds the data created by blocks of sequential order one after the other across all the disks so that the scheme presented by the first block on the first disk, the second on the second, the third to the third, and the fourth to the first, etc. . Therefore, the contents of the file is written in three different disks simultaneously, and hence the higher speed of operation. The block size affects the performance of the system. It is recommended that the disks on the same characteristics. If the system is added to a larger capacity drive or all drives of different capacities available only part of the disc that largest response capacity of the smallest embedded disk. Accordingly, in the event of failure of one of the disks is not good to add disk capacity on the smallest of the existing system, because they will not be able to reach consensus labeling blocks. The total capacity of the field (volume) is equal to the product of the smallest disk capacity and the total number of drives in the field. The system does not tolerate failure of any disk.
- RAID 1 (mirroring) - Offers security to dismissal under the principle of copying the disk contents of one disk to another (several disks), and the system is slow because it constantly copied, especially when writing data. It is suitable for small databases and small systems that require high reliability. Volume is the size of one disk. The system submits failure of one disk.
Volume can be increased by adding the following pairs of disk drives and a field is 1+0 (10) or 0+1, depending on the pairing mode discs. Two pairs of disks are connected by 'striping' principle, and thus linked couples connect in 'mirroring', or vice versa.
- RAID 2 - Based on the coding bits and adding redundant bits upon registration drive, what modern drives have default, ECC control errors. Set of eight bits (byte) adds the ninth bit in a way that is with him total number of 'units' even. No longer in use.
- RAID 3 (byte parity) - Uses parity information to recover from errors and saves them to a special purpose 'parity' drive. Requiring a minimum of three discs, two for data and one for parity. Parity is XOR processing volume data one byte with two discs and a record of the results of processing the parity disk. Writing requires four access drives:
- Reading old data
- Read parity bits
- Entry of new data
- Entry of new parity
It is suitable for applications that require large amounts of sequential data like video. Reading is fast but is slow to enter the calculations and writing parity. Volume is the sum of the data discs. The system submits failure of one disk.
| disk 1 |
disk 2 |
disk 3 |
| |
|
|
| |
|
paritet |
|
Adding additional disks increases the total volume of which is always less parity bills in the size of one disk.
- RAID 4 (cluster parity) - It uses the same principle as RAID 3 but the XOR processing is done on the smallest group of allocation data on disk (Cluster). It is suitable for many small concurrent read operations. Volume is the sum of the data discs. The system submits failure of one disk.
- RAID 5 (block distributed parity) - Enrollment parity distribution solves every disk write, and write speeds up the process because they do not 'attack' just one disc. There is no dedicated parity disk. Parity and XOR processing is done in the field (block) data. Requiring a minimum of three disk (the principle of (principle of processing XOR of two disks for third). Volume is the sum of all drives minus parity records. The system submits notice of one disk.
| disk 1 |
disk 2 |
disk 3 |
| |
|
|
| paritet |
|
|
|
Essential data for efficiency when reading data in a RAID system is field size (blocks, packets) of data. If the data block mali is suitable to work with smaller files, while for videos to favor a larger data set. The diagram shows only three blocks from each disc. Various tests indicate that the optimal field size 32 KB or 64 KB. The concept of the data should not be confused with a cluster (the smallest allocation unit) disk. By adding additional disk drives increases the total volume of which is always less parity entries in the size of a disk (N-1, with n=>3). Configuration is recommended for up to 12 drives installed.
- RAID 6 (block distributed parity) - The same approach as RAID 5, except for entry using two parity disk, not one. A minimum of four drives. Volume is the sum of all drives minus parity records. The system submits failure of two discs, which means increased security.
| disk 1 |
disk 2 |
disk 3 |
disk 4 |
| |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| paritet |
|
paritet |
|
|
The principle of operation is similar to a RAID 5 system. By adding additional disk drives increases the total volume of which is always less parity records two disc size (N-2, with n=>4). It is recommended for configurations with 12 or more embedded discs.
Possible combinations are more fields in the new field of other species so formed RAID 7, RAID 10, RAID 0+1, RAID 30, RAID 50 From the above description shows that the purpose of RAID is not only to increase the volume but also increase safety. If there is a failure of one of the disks in the RAID 3, 4, 5, 6 already at the level of signaling circuitry follows (optical or acoustic or both) that the disk performance and canceled the fall because of extensive XOR record as to reconstruct the data, but the system is still works. By replacing the drive performs the reconstruction of data on the new drive, which can take several hours, and warning signs will stop when the reconstruction finishes. New replacement drive must be formatted before adding if it is already being used in a RAID array to erase blocks of possibly created before, otherwise it could cause system crashes due to misunderstanding of the existing blocks. At formatted (erased) disk by its inclusion in the RAID array reconstruction follows already mentioned blocks. Of course, the entire RAID technology is based on replacing disks "on hot", so no downtime. Commonly in use RAID 0, RAID 1 and RAID 5 disk system connectivity. RAID in any of these combinations using SAN (Storage Area Network) and NAS (Network Attached Storage) systems for data storage. SAN architecture based on the availability of all disks all the servers in the network regardless of where the server (and operating system) are located. NAS architecture is based on installation of drives in a separate device that has its 'operating system' and that is visible across the network as a data storage device, as in the example of home (SOHO) multimedia system in the Chapter of 'Multimedia'.
Not the same kind or the driver circuit of RAID; embedded chip on the computer's motherboard or a separate autonomous unit on the optional card. Completely autonomous controller with its own program support has full control of disks, 'extends' in some way their computer system BIOS BIOS, and represents the operating system as a single disk. Usually contains a diagnostic program support and complete its management of disks that monitors. If you are relying on the RAID drivers incorporated into the operating system and some incomplete support through the motherboard BIOS, this solution is certainly cheaper, but it means that in the case of replacement motherboards computer to another kind of motherboard disc content is no longer visible, which is not very okay. The operating system is easy to install, and the data should be stored, so maybe our better solutions regarding data storage. Serious firm (bank) data storage system will develop into complementary and synchronized systems that are physically different and sufficiently remote locations.
SUMMARY:
RAID system in a server with one or more microprocessors is not sufficient prerequisite for safe storage or quickly large amounts of data or their processing. For this purpose, it is very efficient fast local network of computers connected in a cluster (a group - a cluster), which is presented to the user as a single entity and basically its resources are managed from one place. Its aim is to provide higher availability and reliability (High Availability - HA) or higher-performance (High Performance Computing - HPC) as compared to a stand alone computer, and the result is a super-computer. Specific program support provides a high degree of integration of computers (nodes in the cluster), provides for their coordinated work together and turns them into a single multi-processor system. Cluster is usually based on one type of OS (Windows, Linux ...) and is physically realized as a group of at least two computers, or servers, or mixed. In this way it is possible to ensure the use of significant computational resources for intensive data processing, for example as part of research projects. As this is a group of computers that individually have limited physical resources, extensibility, scalability physical clusters is much higher than expandability computer singletons. Increasing the number of computers in the cluster are almost the same percentage increase in its mean performance. When special connectivity technologies such independent clusters and connect to the network and are grouped in order to obtain the system for collecting and processing large amounts of data or solve very complex tasks (weather forecast, predicting earthquakes, etc.), get the grid - the network again but unified by Tasks which the performance of its nodes, client OS or way of managing resources of individual nodes are not essential.
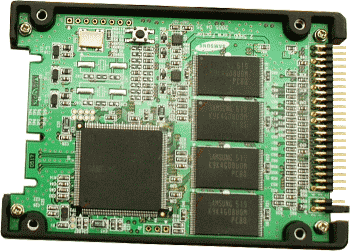
But it seems that time passes rotating disks. Technology, although still expensive, based on flash memory, slowly penetrates into use and replaces the standard electro-mechanical drives. Such 'Discs' called SSD (Solid-State Drive), the speed of writing and reading is roughly twice as high as for conventional disk drives with 10 times less power consumption. So, no moving mechanical parts. Basic use in portable devices where used unit capacity of 32 GB and larger.
|

|
|
Figure*** 3.3.18 SSD disk.
( + / - )
|
|
It is not necessary that the form be as in the previous Figures. Performance without enclosures will surely occupy less space, which is essential for notebooks. Besides, it is significant and greater reliability compared to conventional drives were to consider a mechanical or electronic failure resistance. But no matter what the future holds, the rotating disk and magnetic tape not so quick to 'retire'. In fact, the realization of large-capacity hard disk drive with a standard SDRAM buffer uses FLASH memory in which a large quantity of data is copied from disk to make their availability was faster - SSHD (Solid-State Hybrid Drive).
Citing of this page:
Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia.
{Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file.
Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer
|
