4.1.4. Commands of System |
Controls are the key words that immediately affect the appropriate final action after entering keywords and to pressing the <ENTER> key. Commands per type in keywords and press the key <ENTER> seek additional information or actions to make the final action performed. Commands are short keywords and action is usually quick and easy. Furthermore the description of commands with syntax along with a description of their purpose and method of use:
CHKDSK_[disk:][/F][/V](Ext)
Performs simple diagnostic disk. Switch ' /F ' provides automatic correction of detected defects, and ' /V ' displays the name of the file whose trial is in progress. For example:
CHKDSK A:/V Performs a disk check, asking for correction found errors (none /F) and displays the name test files. DATE_[mm-dd-gg] (Int)
The fit with the brackets changes the current system date. If there is no amendment in parentheses asks to enter the new date. Form may be different if the parameters of the other state.
DISKCOPY_[sourceDISK:_[destinationDISK:]]_[/V](Ext)
Allows copying of disks. The ' /V ' provides control accuracy and copying process takes longer. The destination disk should be pre-formatted.
Examples:
DISKCOPY A: B: /V Allows copying from floppy [A:] to [B:] only if both devices are the same (e.g. both disks of 3.5"), and carries out verification correctness copying. DISKCOPY A: A: Copies the contents of the original disk (SOURCE) to the disk requires that the same inserted into the hole destination (TARGET) and completion deletes currently stored contents of the disc. DOSKEY(Ext)
Usually placed in the starting AUTOEXEC.BAT file to provide memory for about twenty payment orders from the keyboard. Orders are searching and selecting the vertical arrows to re-execute.
EXIT (Int)
Enables output from the OS when the OS came from other applications e.g. from Windows through the DOS window.
LABEL_[disk:][newIME](Ext)
You can change the name of the device (disk). If your device name is not specified by the program asks to enter the new name for the device on which the current OS.
MEM_[/C][/P](Ext)
Provides an overview of the content of working memory. Switch ' /C ' provides a detailed overview and switch ' /P ' desktop print screen by screen.
NUMLOCK=[OFF|ON] (Int)
Specifies the CONFIG.SYS file and determines the initial status of the numeric keypad. The character ' | ' indicates that the choice of OFF and ON mutually exclusive (only one can).
PATH[;] (Int)
Specifies the starting AUTOEXEC.BAT file in the form of a list of directory that will ensure continuous access to separated by ' '. If used during operation, without addition, an overview of the list, and if used with the ' ' deletes set approaches.
PRINT_[/D:device]_#FS_[/P](Ext)
Allows you to print files listed in the specification. The device is one of the printers connected to the serial COM1, COM2, etc., or parallel LPT1, LPT2, etc. (for LPT1 or PRN) port. The ' /P ' allows you to file put on waiting list if you want to print the contents of multiple consecutive files. So have other activities while the files are printed in the order in the list mode. Command makes sense only for a text-readable files.
PROMPT_[$p$g$t$d$v] (Int)
Gives form to prompt (e.g. C:\> or MS-DOS Version 6.20C:\>), depending on how you enroll combinations $p(disc label), $g(label>), $t(time), $d(date) and $v(version OS as in the example). Form is usually set in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file (as in Example III of this Chapter), and less frequently during the work with the OS. Able to command higher than those shown.
SYS_disk:(Ext)
Provides fundamental systemic properties of the device to which it relates. According to the syntax of the command is shown to be set with a device that already has an operating system is the location of the core system files (COMMAND.COM, and the other three). For example:
C:\>SYS A: At diskette [A:] fundamental systemic properties creates and copies the boot sector on it required files (Which?). TIME_[ss:[mm:]] (Int)
Displays (if changes are typed option in parentheses) time, which is currently in the computer's memory. When changes are enough to enter the hours and minutes, although it is possible to add a second and hundreds. Without a parameter displays the current time and asks for a new entry, and press <ENTER> key stops the program.
VER (Int)
Displays the current version of the OS that is installed in the system.
VOL_disk: (Int)
Briefly shows characteristics of the devices to which the command applies.
Edit files
EDIT command allows you to make changes to the files of textual content. The user will have the most needs for harmonization of the file contents:
Specified file is read after power and reach of computer systems on the disk. In one line may be indicated only one OS command and its parameters. To set the correct parameter is useful when you enroll all roads and calls for additional devices used MEMMAKER command that runs a program that successfully support PC and optimizes parameters in these files. Not recommended for novice users to use.
EDIT command in his work relies on program support QBASIC (Quick BASIC) language processor as the composition of the OS. Its activation will show a window in the upper line of the window has the main menu (MENU BAR) who grabbed by pressing <ALT>.
Horizontal arrow selects a menu of the desired (FILE, EDIT, SEARCH, OPTIONS or HELP) or by pressing toward increasing / underlined letter in the menu name. When selecting the desired term or press the corresponding button opens a drop-down menu (POP MENU), which allows retrieval of vertical selection of the desired term.
Terms that have dots (...) after the name indicate the additional choice of choosing.
Meaning of certain terms main menu and its contents listed after:
FILE - choose a file for the work NEW Creating a new file that has no on disk OPEN ... Finding and calling existing file SAVE Storage accessed existing files on the same place. SAVE AS ... Choice of place and name the new file and storage. PRINT... Print all or part of the file. EXIT Exits Editor and return to the OS. EDIT - changes to the selected file CUT Delete selected text and save the contents of the CLIP BOARD. CLIP BOARD Handy once a warehouse for storage. COPY Copies selected text in CLIP BOARD. PASTE Set the content of CLIP BOARD the desired place. CLEAR Delete selected text without placing content in CLIP BOARD. SEARCH - finding the desired FIND... Entering the term that wants to to find. REPEAT LAST FIND Repeating previously found. CHANGE... Entering term that wants to to find and his replacement with new content in part or in whole file. OPTIONS - additional choice DISPLAY Displays and allows modification of parameters editor as background color, font and more. HELP PATH... Allows entry of the device and directory where contains files with additional descriptions (help). HELP - retrieval of additional explanations GETTING STARTED Short instruction on how to use the HELP. KEYBOARD Description of all the choices and combinations of keys. ABOUT... Shows the version of the program and help copyright holders.
With the presented concepts meet is almost inevitable no matter what the application in question, and therefore need to remember. Learn now, you know forever!
Certain commands from the right side and the name have shown that a combination of keys required to perform the same tasks without opening the menu. Work is faster but they should remember. These are called KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS.
EDIT fully screen editor, that allows changing the contents text files (can not open binary) at any location on the screen. Navigating through the contents of the file is done using the editor and cursor keys or numeric sets with deactivated figures. The syntax is:
EDIT_[#FS] (Ext)
For example, a review and possible changes in the content reference MS-DOS to perform the command:
C:\>EDIT C:\DOS\README.TXT
Other commands and orders
Refer to the appropriate tasks groundbreaking advanced users. Mostly they are transient commands and commands and controls the OS. Using them can be realized:
There are a few more features (like FDISK, DBLSPACE) that are appropriate for the use of users who are very good at coping with the OS. It is not recommended to use these commands if you are not beginners several times with the same use a more experienced user.
Do not learn on own mistakes!
SUMMARY:
A short description of each command is given OS command FASTHELP, which has an embedded call control printing from the command MORE. In several screens lists the commands and all commands and their purpose, which is shown in the following consolidated list.
APPEND Allows programs to open data files in specified directories as if they were in the current directory. ATTRIB Displays or changes file attributes. BREAK Sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking. CD Displays the name of or changes the current directory. CHCP Displays or sets the active code page number. CHDIR Displays the name of or changes the current directory. CHKDSK Checks a disk and displays a status report. CHOICE Prompts the user to make a choice in a batch program. CLS Clears the screen. COMMAND Starts a new instance of the MS-DOS command interpreter. COMP Compares the contents of two files or sets of files. COPY Copies one or more files to another location. CTTY Changes the terminal device used to control your system. DATE Displays or sets the date. DBLSPACE Creates and manages drives compressed by using DoubleSpace. DEBUG Starts Debug, a program testing and editing tool. DEFRAG Reorganizes the files on a disk to optimize the disk. DEL Deletes one or more files. DELOLDOS Deletes the OLD_DOS.1 directory and the files it contains. DELTREE Deletes a directory and all the files and subdirectories in it. DIR Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory. DISKCOMP Compares the contents of two floppy disks. DISKCOPY Copies the contents of one floppy disk to another. DOSKEY Edits command lines, recalls MS-DOS commands, and creates macros. DOSSHELL Starts MS-DOS Shell. DRVSPACE Creates and manages drives compressed by using DriveSpace. ECHO Displays messages, or turns command echoing on or off. EDIT Starts MS-DOS Editor, which creates and changes ASCII files. EMM386 Enables or disables EMM386 expanded memory support. ERASE Deletes one or more files. EXIT Quits the COMMAND.COM program (command interpreter). EXPAND Decompresses one or more compressed files. FASTHELP Provides summary Help information for MS-DOS commands. FASTOPEN Decreases the amount of time needed to open frequently used files and directories. FC Compares two files or sets of files, and displays the differences between them. FDISK Configures a hard disk for use with MS-DOS. FIND Searches for a text string in a file or files. FOR Runs a specified command for each file in a set of files. FORMAT Formats a disk for use with MS-DOS. GRAPHICS Loads a program that can print graphics. HELP Provides complete, interactive Help information for MS-DOS commands. INTERLNK Connects two computers via parallel or serial ports. INTERSVR Starts the Interlnk server. KEYB Configures a keyboard for a specific language. LABEL Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk. LH Loads a program into the upper memory area. LOADFIX Loads a program above the first 64K of memory, and runs the program. LOADHIGH Loads a program into the upper memory area. MD Creates a directory. MEM Displays the amount of used and free memory in your system. MEMMAKER Starts the Memmaker program, which optimizes your computer's memory. MKDIR Creates a directory. MODE Configures a system device. MORE Displays output one screen at a time. MOVE Moves one or more files. Also renames files and directories. MSAV Scans your computer for known viruses. MSBACKUP Backs up or restores one or more files from one disk to another. MSD Provides detailed technical information about your computer. NLSFUNC Loads country-specific information. PATH Displays or sets a search path for executable files. PAUSE Suspends processing of a batch file and displays a message. POWER Turns power management on and off. PRINT Prints a text file while you are using other MS-DOS commands. PROMPT Changes the MS-DOS command prompt. QBASIC Starts the MS-DOS QBASIC programming environment. RD Removes a directory. REN Renames a file or files. RENAME Renames a file or files. REPLACE Replaces files. RESTORE Restores files that were backed up by using the BACKUP command. RMDIR Removes a directory. SCANDISK Checks a drive for errors and repairs any problems it finds. SET Displays, sets, or removes MS-DOS environment variables. SETVER Sets the version number that MS-DOS reports to a program. SHARE Installs file-sharing and locking capabilities on your hard disk. SORT Sorts input. SUBST Associates a path with a drive letter. SYS Copies MS-DOS system files and command interpreter to a disk you specify. TIME Displays or sets the system time. TREE Graphically displays the directory structure of a drive or path. TYPE Displays the contents of a text file. UNDELETE Restores files previously deleted with the DEL command. UNFORMAT Restores a disk erased by the FORMAT command. VER Displays the MS-DOS version. VERIFY Directs MS-DOS to verify that your files are written correctly to a disk. VOL Displays a disk volume label and serial number. VSAFE Continuously monitors your computer for viruses. XCOPY Copies files (except hidden and system files) and directory trees. |
A more detailed description of the controls and commands the support program called HELP. Per-call assistance through controls of EDITOR allows the choice of the term using the arrow keys and get a detailed description of the commands and command syntax OS even mali examples of the use thereof. Chance of a direct call to the command e.g.
HELP DIR (should not specify a file type)
Experienced users tend to rely on one of the SHELL, because they do not have almost anything and all actions are performed using the mouse and a few keys. Such programs usually have built-in support for viewing content and characteristics of various types of files, and allow immediate review .dbf or .pcx or other files. These are for example NORTON COMMANDER or XTGOLD.
Phenomenal tool for working with files in DOS environment just NORTON COMMANDER (NC). Its design and inspiration for today's tools the same purpose in a much more advanced operating systems. If it was installed mouse support work with him was even simpler. Red rectangle in the following Figure is the mouse pointer. NC shows the interface of the next image.
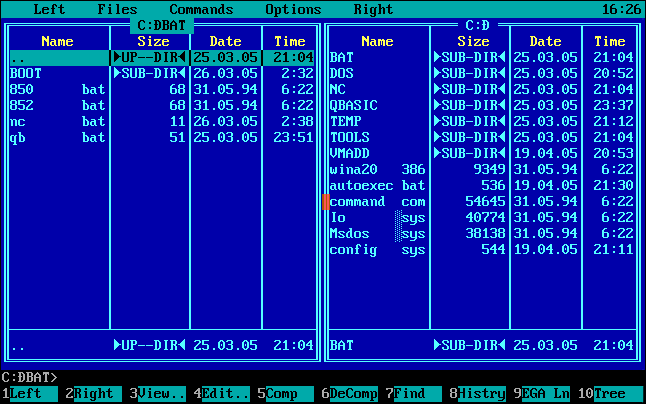
|
Was used a few more versions of DOS (Disk Operaing System) operating system, as well as PC DOS, whose roots are in essentially the same up to version 3.3. MS DOS is a product of the company Microsoft, and PC DOS is the continued development of the same operating system under the aegis of the company IBM. There is no the essential difference between them in the work. But graphical environment under the control of the Windows software is becoming increasingly popular and more efficient (due to the development of technology.) Almost all of today's software tools have a version developed for the Windows environment. WINDOWS environment issue is the next Chapter.
Basic external aid WINDOWS system is a device exactly named MOUSE. Communication mouse comes down to the fact that the mouse POINTER by moving your mouse cursor over the field, and once or twice quickly pressed (clicked) per mouse buttons to order the execution of tasks. As for this, will be used hereinafter abbreviated individual actions with the mouse, as follows:
L1 - The matching of the mouse cursor (POINTER) and ONE-click the LEFT mouse button in order to select a term or icon (small picture of application on Windows) or window. Then the concept, icon or window change color or shape or both, depending on the method of program support. There are no added activities. L2 - The matching of the mouse pointer and DOUBLE-click the LEFT mouse button activate the icon as opening the window which icon represents or does program belongs to icon. L3 - The matching the mouse pointer and icon, or any special graphic sign and HOLDING down LEFT mouse button and simultaneously MOVING the mouse can move the icon or window or 'smears' the window to the desired location or highlights (SELECT), a piece of text, or a list of fields and for leaving key keeps created or labeling changes and issues need of a warrant for the delete-copy depending on the application. When moving the mouse the color of objects along which the cursor moves. Button is RELEASED when the desired object discolored. Then follows the corresponding action, usually copying. The procedure is known as 'DRAG and DROP' (dragging and dropping the object). D1 - The matching the mouse pointer to one of the objects (for example icon) or the content document and ONE-click RIGHT key mouse triggers the action or program or displays an ADDITIONAL choice of choosing belongs. In an additional choice choice is made moving the cursor along the menu and action L1 at certain choice do some activities. Menu breaks with L1 outside its frame or key <ESC>. D3 - The matching the mouse pointer to one of the terms and pressing and HOLDING the RIGHT mouse button, and moving the mouse simultaneous. So move icons or selected content to the destination. When shift the color of objects along which passes. When the over the object you release the button opens an additional choice allows you to select an action with the action L1 at choice. The procedure fits the description of the associated 'L3' (DRAGGING and DROPPING) but with an additional choice. The combination is found in newer Windows applications. K1 - Disposable pressure on the wheel sets marker (label) the window in which the cursor by moving the mouse and the vertical direction to search the active window. One pull any mouse or keyboard termination of this option the label disappears and the display monitor displays the latest status quo. This review is going smoothly, without skipping lines and speed browsing depends on the speed of movement of the mouse. K2 - By turning the dial without pressing done content review active window to jump out of a couple lines without moving the mouse. The default behavior of the mouse can be adjusted by the number of rows. That will be skipped by one 'tooth' when turning wheel. |
Actions K1 and K2 should not expect a default in the Windows 9X operating system. In any case with Windows is more comfortable to work with MOUSE, but if the 'crash' need to know 'DOS' to help them back to life.
The next Chapters will deal exclusively with the Windows graphical environment.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |