Optical communication cable |
UTP cable is an essential component for connecting users to the system. But speeds do not meet the communication between each device when the system is to achieve high speed common basis of the entire system - backbone, or high speed users towards some kind of database system. Then you are using an optical cable - Fiber. All the more widespread use of optical fiber due to its enormous resistance to external electromagnetic influences, especially as the cost price per meter length of optical fiber is decreasing. Technology development is very different. But the two basic groups predominate fiber discussed by way of transmission of light through the light:
To optical interconnects (Fibre Optic - FO) could be used in communications to convert the electrical signal to an optical and vice versa. It works optic converter - TRASCEIVER. How to get through an optical cable can simultaneously achieve communication in one direction only means of communication should be one light transmitter will emit electrical signals into optical signals and transmit them to the Fiber and the receiver on the other side to optical pulses back into electrical form. Communication is simplex. For two-way communication needs two optical fibers and a pair of lines allows full-duplex communication. Therefore the optical connectors for connecting optical fibers can be found in simplex (ST connector) or duplex version (two LC and SC connectors interconnected).
As a light source is used LASER (Light Amplification by Simulated Emission of Radiation), LED (Light Emitting Diode) or laser VCSEL (Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers). Laser is an expensive solution and is used in fiber optic cables narrower core where the light beam at zero angle 'inserts' in Fiber. Use one operating frequency of light, and this mode is labeled monomode (SM). Other solutions use light guides with a core around which the light beam 'inserts' at an angle and use one of several potential operating frequencies of light and this mode is called multimode (MM).
Optical fibers are composed of three basic parts:
Example III
Mode of some kind of optical cable.
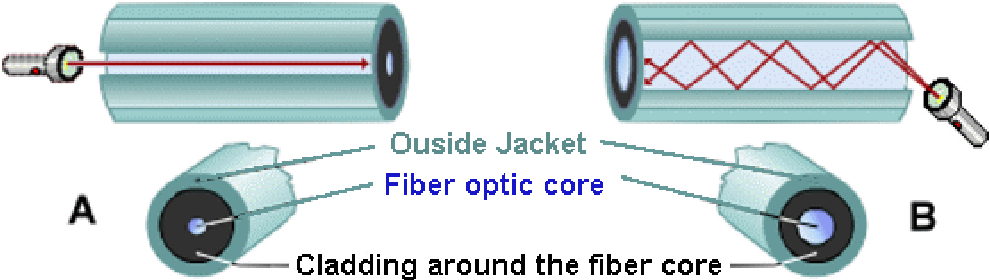
|
| Figure* 3.6.20 Intrusion rays of light in optical cable / Connectors. ( + / - ) |
As this is still a 'glass' components other than the protective layer, it is not advisable to really bend the Fiber. The performances are very diverse, in terms of protection against mechanical damage, moisture and heat. It is clear that it can not be connected fibers of different thickness of the core. The operating frequency can be selected according to the criteria of the best propagation along the fiber, and, in practice, a beam of light of wavelength 850 nm, 1300 nm, 1310 nm and 1550 nm, because the measurements have shown that at these wavelengths minimum attenuation, which falls in the infrared region. The characteristics of the propagation of light in optical fibers in MM greatly affected by how the changes in the refractive index of the core (core with slight change in the refractive index of the edge), and the change in the refractive index of the core and cladding connections. The purpose of changing the refractive index is equalizing the speed of propagation of light rays, ray 'intrusion' at a larger angle has a higher speed of propagation to minimize the difference in time of arrival at the destination in relation to the beams that have been 'intrusion' a lower angle. Thus achieves better preserving the shape of light pulses during the propagation of light rays and hence a greater communication range.
| Core/ Cladding | 10 µm / 125 µm | 50 µm / 125 µm | 62.5 µm / 125 µm |
| Type | SM | MM | MM |
| MOD / Light source | OS1 / LASER | OM1,OM2 / LED | OM1 / LED |
| OM3, OM4 / VCSEL | |||
| Light source | Laser | LED - VCSEL | LED |
| Wavelength (nm) | 1310 / 1500 | 850 / 1300 (OM2, OM4) | 850 / 1300 |
| 850 (OM3) | |||
| Changing of refractive index | stepwise | continuous | stepwise |
According to the table, there was no difference between OM1, OM2 and OM3 at working wavelengths, but the big difference and type of fiber and the frequency range, which is significantly higher in OM3. OM4 is SC-SC Duplex Patch Cable for communication speed up to 100 Gb, optimized for a wavelength of 850 nm. Thus making optical fiber technology is a key factor. This bandwidth optical fiber is determined by the frequency range in which the amplitude of the pulse does not decrease more than half the unit length of 1 km.
|
|
This data is used to calculate the usability features fiber lengthwise. Usability as the value 200 MHz - 1 km can be 400 MHz - 0.5 km or 100 MHz - 2 km and beyond. Shorter fiber has a higher bandwidth. The product defines the possibility for transmission by optical fibers according to length. Commonly used in the local network OM3 optics and VCSEL source. Optical cable operating in this mode has a core width of 50 microns, and more due to the need of such lines in one direction with regard to connecting multiple devices cabinet made with multiple fiber optic strands, or from 4 to 32 or by the cable, where in more than 6 nor make smaller bundles. Therefore this line is often called the multimode optical cable. Connectors used are diverse, and are shown in the Figure above are the most common, but can be selected ST simplex or duplex connector Performance Performance for LC and SC type connectors. Connectors are connected with this particular group of tools and testing fiber optics require complex instruments. Testing of UTP and FO lines should be left to companies that perform setup and connect cables to their corresponding devices.
SUMMARY:
Why Fiber is mentioned along with a network card and wired UTP cable? The vast computing power of the system within a local network requires faster communication and a large flow of data between the key devices in the environment. So great are the requirements to say have a very fast access to a group of servers. To this end, the servers will be installed optical network card, especially if it is a system for storing massive amounts of data (Data Storage System), or system like SAN (Storage Area Networks). To certain types of fast fibers have traditionally differed with the label width cores on the cable sheath and use a different color of the protective coating optical fiber. Thus, the optical fiber coatings for SM usually yellow (OS1), for MM is orange (OM2), blue (OM3) and aqua (OM4), and for use outside the building they have black painted armor with built-in supporting steel wire in the armor.
Previously described network card does not have to be just an expensive privilege server. Usually a PC can become its 'owner' if the need arises that a computer has very fast access to datacenter. Of course, the optical connection should be monitored and appropriate devices that communicate over optical fiber, and that incorporating transceiver, either as a unit or as part of an increasingly popular module as module SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable Interface Converter). Not only does the network card does not have to be a wired connection, but may contain a complete system for the wireless connection, for example through the 802.11g standard with built-in hand-transmitter and a small antenna. This form is especially popular with laptops, either as a built-in PCMCIA or ExpressCard or USB accessory.
As with fiber optic cables are used at Ethernet communications, the same principle as for wiring codes are 10Base-F, 100Base-FX or 1000Base-LX. As optical communication is 'privilege' of professionals, stated enough as an illustration.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |