ITX motherboard - Chipset Intel z370 |
 Mini-ITX is motherboard with approximate dimensions of 170 mm × 170 mm, developed around 2000. They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems, like as at Figure 3.5.61b. Originally, they were a niche product, designed for fan-less cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience. Mini-ITX boards primarily appeal to the industrial and embedded PC markets, with the majority sold as bulk components or integrated into a finished system for single-purpose computing applications. This mini motherboard became possible when lithography technology enabled chips with low thermal dissipation, according to description in Chapter of Chip. Better lithography enabled small family of ITX motherboards as at introductory Figure of this paragraph (Nano-ITX : 120 mm × 120 mm, Pico-ITX : 72 mm × 100 mm, Mobile-ITX : 45 mm × 75 mm). But, small motherboard doesn't mean cheap and weak system, according to next picture it can be very powerful.
Mini-ITX is motherboard with approximate dimensions of 170 mm × 170 mm, developed around 2000. They are commonly used in small-configured computer systems, like as at Figure 3.5.61b. Originally, they were a niche product, designed for fan-less cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience. Mini-ITX boards primarily appeal to the industrial and embedded PC markets, with the majority sold as bulk components or integrated into a finished system for single-purpose computing applications. This mini motherboard became possible when lithography technology enabled chips with low thermal dissipation, according to description in Chapter of Chip. Better lithography enabled small family of ITX motherboards as at introductory Figure of this paragraph (Nano-ITX : 120 mm × 120 mm, Pico-ITX : 72 mm × 100 mm, Mobile-ITX : 45 mm × 75 mm). But, small motherboard doesn't mean cheap and weak system, according to next picture it can be very powerful.

|
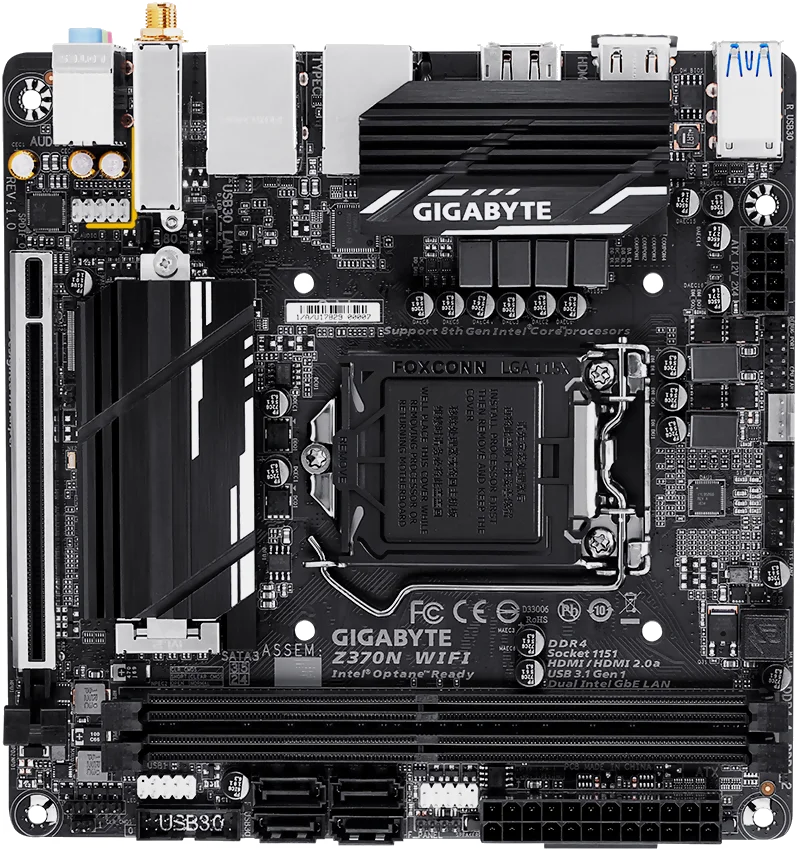
| Figure* 1. GIGABYTE 'Z370N Wi‑Fi' motherboard. ( + / - ) |
Key Features of this motherboard is HDMI 2.0a 21:9 / HDR, PCIe bifurcation support, Intel USB 3.1 Gen1 with USB Type-C™, Dual Intel GbE LAN with 25KV protection, 2×2 11ac Wireless, Dual M.2, RGB Fusion, Smart Fan 5. Other features are:
The GIGABYTE Z370 Platform is the first enthusiast platform that supports Intel’s latest Optane technology. Optane fuels storage performance by acting as a cache drive giving users a significant boost compared to traditional mechanical drives. GIGABYTE is offering a tested and proven platform that ensures proper compatibility with profiles up to 4400 MHz and beyond. All users need to do to attain this performance boost is to ensure that their memory module is XMP capable and that the XMP function is activated and enabled on GIGABYTE motherboard. All components are newest technology achievements. Monster!
Next Figure shows back connectors of motherboard. Almost everything what have 'normal PC'.
 |
| Figure 2. Back Connectors of GIGABYTE 'Z370N Wi‑Fi'. |
At the first look difference is:
As chipset is Intel z370, only 8th generation of microprocessors is supported, as next table shows.
| Chipset Intel® z370 - Socket LGA 1151 v2 (14 nm Lithography - Coffee Lake) | ||||||||
| Intel® CPU for motherboard | Model | Z370N Wi‑Fi |
||||||
| PCB | 1.0 | |||||||
| CPU Model |
CPU Frequency |
L3 Cache |
GPU Frequency |
Step | TDP | BCLK | Since BIOS Ver. | |
| Core i7-8700K |
3.70 GHz | 12 MB | 350 MHz / 1200 MHz |
U0 | 95 W | 100 | F1 | |
| Core i7-8700 |
3.20 GHz | 12 MB | 350 MHz / 1200 MHz |
65 W | ||||
| Core i5-8600K |
3.60 GHz | 9 MB | 350 MHz / 1150 MHz |
95 W | ||||
| Core i5-8400 |
2.80 GHz | 9 MB | 350 MHz / 1050 MHz |
65 W | ||||
| Core i3-8350K |
4.00 GHz | 8 MB | 350 MHz / 1150 MHz |
B0 | 91 W | |||
| Core i3-8100 |
3.60 GHz | 6 MB | 350 MHz / 1100 MHz |
65 W | ||||
Intel had several reasons for introducing the LGA 1151 v2 microprocessor socket of the 8th generation microprocessor with slightly different functions of some pins and therefore the incompatibility of the new microprocessor and chipset with the predecessors. One of them is the ability to work with more multiple cores, because AMD has been overtaken by the above. In addition, some groups of microprocessor transistors are physically increased in order to achieve better performance. The result is a better microprocessor optimization and a higher operating frequency, as well as a physically slightly larger chip (die) of microprocessor. In addition, the chipset fully supports the latest technology of peripherals. It is possible that changes were made to make it less difficulty in the transition to finer process of development that AMD is already using. This is the first time after a long time that AMD 'skipped' the competitor.
As shown in Figure 1. there is lot of connectors at the motherboard, which means must have case where to put other components (power supply, brackets with connectors ...). That case may be small (type BAREBONE), but if consider holes at motherboard it is fully compatible for ATX case. Chipset z370 has features shown at next table.
| Essentials of Chipset Intel® z370 | |
| Product Collection | Intel® 300 Series Chipsets |
| Code Name | Products formerly Coffee Lake |
| Status | Launched |
| Launch Date | Q4'17 |
| Bus Speed | 8 GT/s DMI3 |
| Lithography | 22 nm |
| TDP | 6 W |
| Supports Overclocking | Yes |
| Supplemental Information | |
| Embedded Options Available | No |
| Conflict Free | Yes |
| Memory Specifications | |
| # of DIMMs per channel | 2 |
| Graphics Specifications | |
| # of Displays Supported ‡ | 3 |
| Expansion Options | |
| PCI Support | No |
| PCI Express Revision | 3.0 |
| PCI Express Configurations ‡ | x1, x2, x4 |
| Max # of PCI Express Lanes | 24 |
| I / O Specifications | |
| # of USB Ports | 14 |
| USB Revision | 3.0 / 2.0 |
| USB 3.0 | Up to 10 |
| USB 2.0 | Up to 14 |
| Max # of SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 6 |
| RAID Configuration | PCIe* 0, 1, 5 / SATA 0, 1, 5, 10 |
| Integrated LAN | Integrated MAC |
| Supported Processor PCI-e Port Configurations | 1×16 or 2×8 or 1×8+2×4 |
| Package Specifications | |
| Package Size | 23 mm × 24 mm |
| Low Halogen Options Available | See MDDS |
| Advanced Technologies | |
| Intel® Optane™ Memory Supported ‡ | Yes |
| Intel® Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O (VT-d) ‡ | Yes |
| Intel® vPro™ Technology ‡ | No |
| Intel® ME Firmware Version | No |
| Intel® HD Audio Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Rapid Storage Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Rapid Storage Technology enterprise | No |
| Intel® Standard Manageability | No |
| Intel® Stable Image Platform Program (SIPP) | No |
| Intel® Rapid Storage Technology for PCI Storage | Yes |
| Intel® Smart Sound Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Platform Trust Technology (Intel® PTT) | Yes |
| Security & Reliability | |
| Intel® Trusted Execution Technology ‡ | No |
| Intel® Boot Guard | Yes |
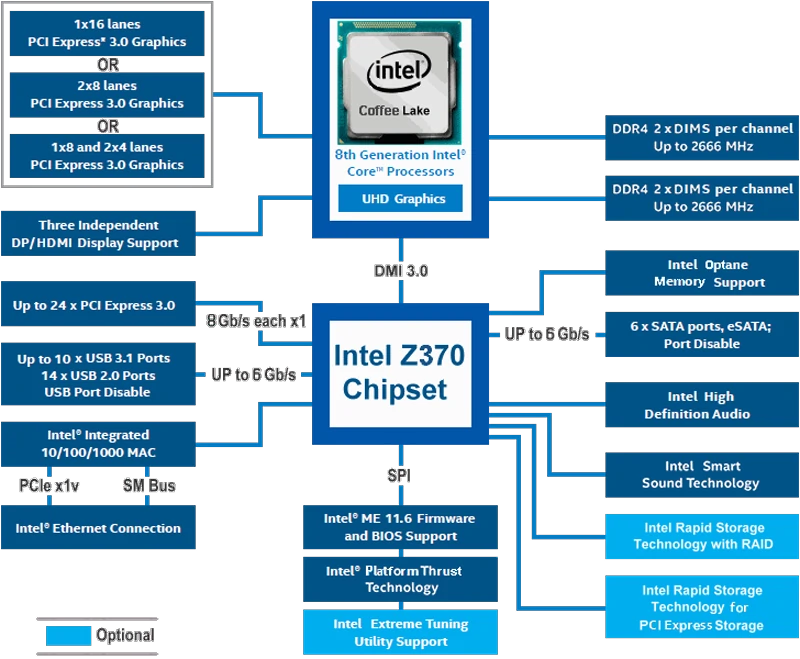
Block-schema of the chipset z370 is shown on the animated Figure 3.5.44a for comparison with the predecessor, and here is also here separately compared to its upgraded version z390 in the same 22 nm lithographic process:
|
| Figure* 3. Blok-schema of Chipset Intel z370 / 390. ( + / - ) |
Overall, most of the changes to the z370 chipset is relatively minor. Obviously the support for the new 'Coffee Lake' CPU is a very big deal, but the odd thing is that for whatever reason Intel decided not to change the physical socket from LGA 1151. This means that you can install a 'Coffee Lake' CPU into a z270 motherboard without the need of a hammer and everything will appear to be correct - only the system will never actually be able to POST (Power On Self Test) and operate correctly, the system would not actually function. The purpose of this incompatibility is not clear for the time being. As opposed to that, the seventh-generation microprocessor supports quite a number of different architectures (Celeron, Pentium ...). Is it the generation shift or is the eight generation of microprocessors and PCH just exclusive?
There are lot of movies about this chipset and motherboard format at 'YouTube', but what impress me is 'Gigabyte GB-BNi7HG6-1060 - Mini-PC Barebone (BRIX)'.

|
| |
|
| ||
| Figure 4. Gigabyte BRIX |
Basic features are:
Very impressive. Of course, motherboard and other elements are not of some usual ITX standard, but special design of Gigabyte. Very powerful computer (PC?). Power supply and antenna are not shown at the Figure. Those are separate devices.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/specific/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |