3.5.10. Motherboard |
Although the microprocessor component that most people most identify with PC because of its major impact on system performance, an essential part of the computer is responsible for all of the motherboard (motherboard). On it's almost everything you need to computer can perform basic tasks, especially if it has a chipset with graphics system. Components that she needs to add the microprocessor, working memory, optical disk device, and the device, and everything is placed in a casing with an adapter. Floppy device still be added to the emergency, but instead it more fitted device for reading various types of memory cards like card of digital camera and other similar devices. The quality and characteristics of additional components may be the overall cost of PCs increased many times over. If the installation of a powerful graphics card and obtain the components that will meet the 'ability to perform a' total cost PCs tremendous growth rate, three times or more compared to a computer for office use. When added to the monitor, keyboard and mouse to the PC computer system is available for use. The motherboard is a large expenditure in relation to the total cost of the computer system and it is not advisable to economize. Manufacturers usually have the same model offered several different versions so you can choose the solution according to the needs and appreciates.
The motherboard's BIOS (Basic Input Output System), whose function is to combine all the components into a functional whole. Today's versions are derived as FlashROM so that the observed defect in the program code can be easily corrected. Precisely through regular periodic issuance of the Internet 'patch' program code BIOS and new versions of the device drivers on the motherboard, recognized quality manufacturer of motherboards. Good BIOS is essentially a well-made pipe in the irrigation system, which is not likely to happen after commissioning of water leaks or drips or runs. In its work, the BIOS uses the parameters in the form of data recorded in its CMOS memory on which knows how to handle the individual components and devices, it is necessary data easily changed or deleted entirely. The correctness of the entered data in CMOS is monitored by calculating the control number (checksum) that is not right if the current version of the BIOS is reading a different data structure than expected, or if they are stored in CMOS illegal or impossible parameters for a device. If the data in CMOS deleted, the computer boots, enter the CMOS default parameters, which can then modify as needed (date, time ...). BIOS system as a link between the OS and the hardware is overcome, and the newer generation of computers use motherboards that contain UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), more modern interface between the OS and hardware with advanced capabilities that fully retains compatibility with the BIOS.
Motherboards are basically differentiated by the type of processors that is built today is focused on two concepts: AMD or Intel-oriented motherboard, to the most important producers of microprocessors. But everyone has one thing in common, the PCI-Express bus (PCI-E, PCIe). Chipset and still have support for standard PCI cards to be 'old' cards do not throw (TV card, A/D converter, modem ...). AGP port which supports rare type of motherboard PCI-Express, AGP port has definitely gone to 'retire'. In a similar way, 'retired' the ISA bus, namely the first PCI motherboard had the chipset support for ISA cards with several ISA slots, which eventually completely eliminated. However, there are still manufacturers that make the motherboard with inserted ISA slot, to allow the 'old' expensive peripherals work (like some very precise and very expensive A/D and D/A converter, but it needs to multiply more pay . specificity in relation to the following description of the server motherboard, but it should remain fun for professionals in the field.
PCI-Express the successor to the PCI bus. Works under the principle of association of one or more corridor (lane), 'width' of the sign, 8 bits, into a single hub. It is a serial bus with separate pairs for data transfer as 'characters' in both directions in every corridor of low-voltage signaling. Outgoing traffic is coming from and separate, each in its channel within a single corridor - FULL DUPLEX. One corridor (x1) is about four times faster than standard PCI bus, and using multiple corridors (x2, x4, x8, x16 or x32), you can significantly increase the throughput. Each corridor has a bandwidth of 500 MBps and 250 MBps per direction. Besides devices designed for operating in x1 slot may work for example x8 slot, which means that it is secure, and physical and electrical compatibility for devices with smaller requests for bandwidth. 'Minor' card uses only corridor available in the 'bigger' slot. But when you look at the pin's slot for the card you see only two pins for the reception and two-pin and to teach in one corridor.
| Side B | PIN | Side A |
| +12 volt power | 1 | Hot plug presence detect |
| +12 volt power | 2 | +12 volt power |
| Reserved | 3 | +12 volt power |
| Ground | 4 | Ground |
| SMBus clock | 5 | TCK |
| SMBus data | 6 | TDI |
| Ground | 7 | TDO |
| +3.3 volt power | 8 | TMS |
| +TRST# | 9 | +3.3 volt power |
| 3.3v volt power | 10 | +3.3 volt power |
| Link Reactivation | 11 | Power Good |
| Mechanical barrier | ||
| Reserved | 12 | Ground |
| Ground | 13 |
Reference Clock Differential pair |
|
Transmitter Lane 0, Differential pair |
14 | |
| 15 | Ground | |
| Ground | 16 |
Receiver Lane 0, Differential pair |
| Hotplug detect | 17 | |
| Ground | 18 | Ground |
Bits are transmitted serially on the principle of 8B/10B encoding. Purpose 8B/10B encoding is transforming the character of 8 bits in this new format of 10 bits for better synchronization between the reception and transmission, control, fault management and transmission. Further acceleration as specified coding scheme can be used 3B/4B and 5B/6B when a lot of the leading "0". Overall score is much higher coding rate. Slot on the motherboard for a PCI-Express card provides the first 11 pairs of contacts (PINs) for managing, powering and signaling, while the next couples pin this go in groups of corridors for incoming and outgoing traffic, and each group has a pin for detecting devices (hotplug detect). Of pairs of pin's 12-18, according to the previous table continues after nearly seven pairs PINs for each corridor. And there is no +5 V supply. Pin 1 is of course to the rear edge of the motherboard. In relation to the concept of bus shown in Figure 3.5.4 is a very significant difference. Of course, the standard is constantly evolving and gradually penetrates version 3, and the development of a version 4. Characteristics of the different versions is as follows.
Baud Rate in version PCI-Express v2 is increased by corridor on 5 GTps (gigatransfers per second), with the 8B/10B encoding scheme. PCI-Express is used with v3 128B/130B coding scheme which is based on the transfer of a large volume of data between the data needed for synchronization and thanks to advanced system synchronization when transferring data (PLL - phase-locked loop), it is possible to improve the 8 GTps. Therefore, to increase the bandwidth, the key factor is the improvement of the technological process of chip production and, based on that, the improvement of communication protocols. Because of the two-way exchange of data and of data that relates to synchronize the actual transfer rate is slightly lower, about 20% up to version 2 and less than 2% in the coming versions. Specifications for the PCI-Express v4 and PCI-Express v5, are still impressive.
The peculiarity 'hotplug' technology - insert the card into the computer system while the computer is running with additional slot for inserting a new card types - ExpressCard in laptops (notebooks). Cards should have a thickness of 5 mm and a width of 34 mm and 54 mm. These cards are designed to work with the version of the USB interface. All are likely to PCMCIA cards and other similar types of card slightly into oblivion.
On a similar philosophy associated 'northern' (MCH) and 'southern' (ICH) chipset, and memory bus itself has undergone significant changes. Used simultaneous multiple channel access memory and DDR (Double Data Rate) memory modules manufacturing technology that allows it to multiply the clock speed transfer of data in relation to the clock speed of the memory, in order to ultimately increase the overall throughput by working memory. Moving driver memory system physically and logically into the case of microprocessors, as well as the concept of Intel X58 (Figure 3.5.26c) and Intel X79 platform to achieve even better results, and in addition to faster access to the graphical resources is achieved by the concept of the Intel Z77, Z87, Z97, Z170, Z270 and newer platforms that completely eliminates need for MCH chip. PCI-Express bus eliminating the need for the AGP port, which is the variant x16 overwhelmingly surpasses rights as a bus, if necessary, the simultaneous use of multiple graphics cards. In the following Figure 3.5.26b shows the system with two 'x16' slot for graphics cards.
Intel NM10 series platform designed for use on microprocessors series 'Atom' in which the graphics processor is physically and logically incorporated in the same casing, with the CPU, and allows the design of very small computers by dimensions, where the graphics resources are of no significance. It is not surprising development of computer systems with all the devices installed in the chassis monitor (All-In-One concept), even with the solutions that have monitors with screens that detect touch. The solution is very suitable for office use. For this purpose designed and Q57 chipset that uses the second generation 'Core' process which is an independent body added graphics support, CPU and GPU are separate subsystems. Integrated graphics subsystem operates using part of physical RAM, and the operating system is deprived of the resources. This solution is good if the computer is used for less demanding purposes or 'first hand' if the motherboard has a x16 slot for graphics card. Retrofitting an independent graphics card with its own memory resources should be in the BIOS disable the integrated graphics. Third generation 'Core' processors has physically and logically integrated processor and graphics boards, it's all one integrated whole, the CPU and GPU are integrated subsystems.
Although innovation is at the socket of the slot and fast synchronous serial communication is of great importance, in the instructions for assembling the graphics card is something like: 'insert the card into the slot gently and evenly'? No wonder he dropped out of the reservoir if the computer casing a bit upside down (cheap) done. Where is the time ISA slots! With its wide, golden and firm contact feathers! Therefore, we should use a motherboard with integrated graphics card holder, to provide high quality enclosures with good power - an energy source due to significantly increased consumption of the device, particularly microprocessors and graphics cards. And 'North Bridge' gladly requires some power (see at heatsink in the Figure). Caution when purchasing; advertised power of 1000 W to furnish 1000 W no matter, whatever we think about this.
Although the valuation is based on the computer's microprocessor and its capabilities, can not be neglected role of expensive electronic components integrated into one or more integrated circuits (CHIPSET) whose task is to successfully manage and exchange data between different computer devices. As the microprocessor and other devices so technologically developed and pre chipset growing task that must be done successfully. As there are different types of processors so the chipset is made by them. Very interesting is the trend that most of the devices are basically added to the motherboard as a separate card is now integrated into the motherboard CHIPSET or additional integrated circuit board (network, music, graphics ...). Cancellation of any of them mean the same best hand off in the BIOS of the motherboard and adding a new device to one of the most anticipated slot's. But what is important is that the price of motherboards for office computers acceptable and possible defects may not be a big outlay.
Example VII
One of the most powerful solutions to support multi-core microprocessor family from INTEL, for home and office use with the motherboard chipset Intel X48 developed for the PC system with support for microprocessors type Core 2 Duo, Quad and Extreme, which is the base processor in LGA 775 version. Set logic chipsets is usually divided into two parts:

|
| Figure 3.5.26** Block Diagram Intel-X48/X58 chipsets / Intel DX48BT2 motherboard. ( + / - ) |
When choosing a motherboard should be careful of the version, because some do not support RAID technology, although they have more SATA-II ports for disks (e.g. ICH9 / ICH9DH not supported, and ICH9R / ICH9DO supported), if this is to use multiple disks in RAID arrays. Before purchasing the motherboard must be carefully study the instructions, which is not lacking in the Internet.
Displayed motherboard chipsets no longer support for standard serial RS 232C interface and PIO interface, PS/2 ports for mouse and keyboard, as well as the connector for FDD drive (floppy) in the displayed version of ICH, although supported, it does not mean that devices using such an interface can not be connected because there are different types of adapters or a card just for this purpose. These logic circuits are designed as two separate chips, but in the future can expect their consolidation into one common unit. Throughput PCI-E x16 is 16 GBpss, and the X48 MCH and processor can communicate with the FSB running at 800/1067/1333/1600 MHz DDR3 and the working memory. Utilization of MCH in this sense is related to the working memory and faster processor with a higher FSB clock rate, then the price. MCH and ICH communicate with 2 GBpss PCI-E x4 in essence should not be so long because most of the connector ports provided for the length of x16 is not a function, but it is set higher connector for typing of production (lower costs).
Chipset is not intended for this kind of performance the average office computer and the 'North Bridge' has no built-in support for graphics, but must use one or two composite video card. Therefore, in the following Figure shows the connector interface two graphics cards, and in size compared with the interface card in Figure 3.5.9c can be concluded that the cards are shown in the following example, a low-profile height, suitable for installation in thin 'desktop' casing . The peculiarity of the presented card with a VGA connector and HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface). Characteristic of this interface is that it allows transmission of video and audio files to newer TV sets and allied equipment, that transmits video and audio via a single cable. Only newer chipsets and graphic cards and operating systems support this option. Quality cable allows transmission of this signal at distances greater than 10 m, and the corresponding signal conversion devices (extender) can be achieved transmission of signals over UTP cable length 50-100 m
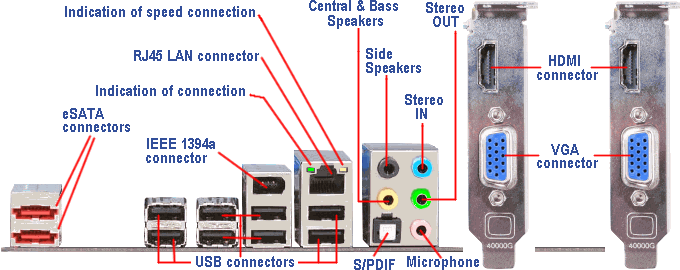 |
| Figure 3.5.27 I / O ports of PCI-Express motherboard. |
Thus, an important feature in relation to the chipset's from earlier periods is totally dominated USB concept as a mechanism connecting peripheral devices to a computer, the LAN and Audio devices are inserted on the motherboard, as well as significantly increased throughput capacity of all the buses in the second revision of the PCI-Express standards. The motherboard has an image with software that allows you to fine tune some of the basic components (microprocessors, bus and memory) with regard to 'overload' (overclocking) individual components in accordance with the efficiency of their cooling systems. Specifically, are adjusted operating frequency processors, graphics cards, or other components of the computer beyond factory settings. It can be traced heating components and fine adjustment of parameters to achieve the best possible performance in accordance with the circumstances.
Although the pictures 3.5.26b and 3.5.27 see a multitude of connections, all without fear because they can connect all the major ports physically different. This is one of the most anticipated precautions manufacturers and designers of standard connections. It should be a great power to a connector to connect to the wrong port. Connecting the connector must be able to make a 'two-finger', without the use of a great power, and if not how to attach a cloth it is possible that some of these pin-connectors are bent or broke what is a foreign body in the connector or something. The same goes for the power connections on the motherboard and the devices as well as slots for memory cards or modules. DDR or DDR2 memory module can be inserted into a DDR3 slot or PCI-E card can not be inserted into a standard PCI slot and so on. Physical layout of the different types of slots on the motherboard Figure 3.5.7 illustrates the confusion is almost impossible.
Motherboards PC compatible computers are manufactured in several different sizes, which are standardized (recommended), and among other prescribed place of card slots and places holes for the screws. But not all manufacturers put 'holes' in the same place and therefore should be taken when replacing the motherboard. Basically we offer two formats motherboards: ATX (successor to AT format) and BTX. In relation to the format of AT ATX format has brought several significant changes, such as electronic power switch so the computer can shut down the operating system, advanced layout components on the motherboard and integrated connectors such as parallel and serial ports on the rear side ATX board. It's basically simplify the assembling computers. BTX format would in the coming years to replace ATX format. Will it happen, time will tell, and there is less likely to want, because the third generation of microprocessors manufactured in 32 nm technology much less heat, especially the fifth generation of microprocessors manufactured in 14 nm technology, and quite a bit of heating have versions for mobile devices.
|

|
| Figure** 3.5.28 ATX and BTX layout components of PC. ( + / - ) |
The main difference in ATX and BTX format is scheduled basic elements motherboard, rear interface, expansion slots with cards, slots for memory modules and prospecting microprocessors. BTX has recently been proposed schedule by Intel that would in essence should provide better cooling components, which for AT format is not a problem because the former components are not very heated, for example, microprocessors are spending less than 25 W and the graphics card about 10 W. By BTX specification should provide a dedicated cooling system for cooling and ventilation, thermal module - TM (Thermal module), which directs the flow of air across the heatsink microprocessor, and attaches to the SRM module (Support and Retention module) on the casing. SRM module is molded metal base that stands between the motherboard and the casing to reduce the distortion of the motherboard into the microprocessor, resulting from warming.
These dimensions of ATX motherboard specification applies to the version 2.2 and previous versions of specifications to predict the motherboard smaller than the above, and with the usual PCI slots and a few ISA slot as the specification version 2.01. Specifications include requirements for power supply (connectors, voltage, voltage tolerance ...). Let the following specifications will probably 'retire' and standard PCI slot when the market is dominated by card type PCI-Express. These dimensions of BTX motherboards are as specified in version 1.0b.
There are formats motherboards out above, which are usually internal resolution of a manufacturer as the body in which it is located. Nonstandard casing, power supply and motherboard can lead to subsequent problems in maintenance. Therefore, these special facilities should stay out of this review. To this group belong formats workstations and servers such as the Extended ATX (EATX), Enhanced Extended ATX (EEATX) Workstation ATX (WATX) or ATX Server (SWTX) who have dimensions larger than a standard ATX format.
SUMMARY:
TEMPERATURE of the device is now a significant problem that needs to be taken into account in the design of a PC, and it is effectively solved in the BTX conception. ATX motherboard in full (full) version is extended to the left relative to the displayed image, and BTX motherboard was extended to the full version, or reduced to 'pico' version to the right relative to the chart in Figure 3.5.28a.
Essential innovations in the concept of a BTX thermal module for cooling the CPU with a directional air flow from the front a computer directly to the CPU and the exit of the thermal flow through the heatsink module MCH chipset, and change the motherboard in the 'tower' case. Eh, these temperatures! Everything is acceptable as it never heats up more than 55°C, measured on a heat sink or chassis devices. Inside the chip (core) temperatures are much higher, up to 150°C. So BTX motherboard can not ATX chassis. Some manufacturers produce upright ATX / BTX compatible case in which the BTX motherboard on the same side of the body as if it comes ATX board, only changing rear apron, which is not BTX specification to version 1.0b. Neither the position of TM and SRM was not according to the specification, but are always in the same place in the casing, regardless of the size of the motherboard and the height of the casing. How to facilitate installation of all three types of BTX boards in upright body it is possible that it will remain so. TM and SRM module option that usually have to pay extra. In addition to a significant reduction of distortion due to temperature, motherboard, SRM module reduces stress and compensates for vibrations caused shock.
However, better lithography (14 nm) has considerably reduced CPU heating, so the BTX concept did not survive. The only thing that has been taken from this concept is the addition of a metal base on the underside of the motherboard embedded in the socket of CPU, as shown in Figure 3.5.28c. At the same time, better lithography enabled the Mini-ITX motherboard format to take up a small part of the market.
Motherboards for servers do not have such a strictly defined formats except for the location of the rear interface card and the recommendations for PC compatible computers. And when you look at the inside of one of them can not be well resolved not to notice the ventilation system which ensures an efficient continuous working. However, servers are not personal computers, they are a special kind of hardware, such as DRAM and chipset that is built is not the same properties as for the PC.
As the technology of microprocessors evolved, have changed and concepts of making motherboards, in a way that modern microprocessors more powerful and have a built-in integrated graphics support, unlike appended graphics microprocessor as shown in Figure 3b, and is eliminated quite functions for which MCH together with the ICH combine into a single chip - PCH. Figures 3.5.31, 3.5.33, 3.5.37, 3.5.44 and 3.5.44, also Figure 3.5.61 which describing the 'weaker' microprocessor, illustrating the growth possibilities of newer technologies. It is expected that in the future PCH move into case of microprocessor, and become his physically and functionally integrated part.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |