PCI-Express 4.0 Motherboard - Chipset Z590 |
 First PC was made by IBM in August 1981. It was based on an open, card-based architecture with seven slots, which allowed third parties to develop own cards for it. It used the Intel 8088 CPU running at 4.77 MHz, containing 29'000 transistors. No fans inside desktop case. Open based concept was the reason for it's quickly accept on the market, and became more popular than other 'closed' platforms (like Apple, Commodore, Spectrum, Atari ...). First laptop, similar to today's laptops, was Compaq Armada at the late 1990s. Around 2010, laptops took over the dominance of the PC market. Therefore, it is not surprising that today the development of microprocessors is primarily focused on mobile devices.
First PC was made by IBM in August 1981. It was based on an open, card-based architecture with seven slots, which allowed third parties to develop own cards for it. It used the Intel 8088 CPU running at 4.77 MHz, containing 29'000 transistors. No fans inside desktop case. Open based concept was the reason for it's quickly accept on the market, and became more popular than other 'closed' platforms (like Apple, Commodore, Spectrum, Atari ...). First laptop, similar to today's laptops, was Compaq Armada at the late 1990s. Around 2010, laptops took over the dominance of the PC market. Therefore, it is not surprising that today the development of microprocessors is primarily focused on mobile devices.
Accordingly, the development process of the microprocessor is no different with Intel. Intel's Tiger Lake is codename for the 11th generation Intel Core mobile processors based on the new core microarchitecture, manufactured using Intel's third-generation 10 nm process known as 10SF (10 nm SuperFin). Tiger Lake replaces the Ice Lake family of mobile processors, representing an optimization step in Intel's process–architecture–optimization model. These quad-core processors are designed for 'ultraportable gaming' laptops with 28-35 W TDP (Thermal Design Power).
With a small TDP everything is easier to do, but for powerful computers the situation is different. It is not easy to make a powerful processor for an ATX platform computer. There is a big 'battle' between AMD and Intel over this. Everyone else is 'out of the game'. Intel's contribution is greatest in server platforms, but also in the introduction of new technologies that enable more versatile use of home computers. Their latest chipset 'z590' in community with the processor can support almost anything without the need to use an seven-slot motherboard. Therefore, it was difficult for the author of this page to find an ATX motherboard that would effectively support the use of slots without, for example, a graphics card 'covering' one slot and making it unusable.
Regarding the above, the choice of the author is the MSI (Micro-Star International) motherboard. MSI has the following motherboard categories in its program:
The author's choice is 'MPG Z590 GAMING FORCE' motherboard, without using Wi‑Fi 6 capabilities, because in the opinion of the author this feature should have SOHO gataway. But first let's look at what Intel's 'z590' series offers.
Example XVI
In this example shown in the block diagram of the chipset z590. Shown in the example motherboard supports Core i3, Core i5, Core i7 and Core i9 microprocessors of tenth and eleventh generation planned with the socket LGA 1200.
| Intel® Core microprocessors (14 nm Lithography) | ||||||
| Product Name |
Core i9 10900 K |
Core i7 10700 K |
Core i5 10600 K |
Core i9 11900 K |
Core i7 11700 K |
Core i5 11600 K |
| Code Name | Comet Lake - S | Rocket Lake - S | ||||
| Chipset | series 4XX (5XX) | series 5XX | ||||
| PCIe support | 3.0 | 4.0 | ||||
| Socket | LGA 1200 | LGA 1200 | ||||
| Performance | ||||||
| # of Cores | 10 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 6 |
| # of Threads | 20 | 16 | 12 | 16 | 16 | 12 |
| Base Frequency | 3.7 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 4.1 GHz | 3.5 GHz | 3.6 GHz | 3.9 GHz |
| Turbo Frequency | 5.3 GHz | 5.1 GHz | 4.8 GHz | 5.3 GHz | 5.0 GHz | 4.9 GHz |
| Smart Cache | 20 MB | 16 MB | 12 MB | 16 MB | 16 MB | 12 MB |
| Bus Speed | 8 GT/s DMI3 | |||||
| TDP | 125 W | |||||
| Memory Specifications | ||||||
| Max Size | 128 GB | |||||
| M.2 Memory / Storage | No | Yes | ||||
| Memory Types | DDR4 - 2933 | DDR4 - 2666 | DDR4 - 3200 | |||
| # of Channels | 2 | |||||
| Bandwidth | 45.8 GB/s | 41.5 GB/s | ||||
| ECC Support | No | |||||
| Graphics Specifications | ||||||
| Processor Graphics | UHD 630 | Intel Iris Xe | ||||
Spending five generations on the same base microarchitecture is a long time. Progress and excitement can be sustained through optimizing a process node, adding cores, and extracting every 'drop' of frequency, but at some point the base design becomes the bottleneck and it is time to move on. Intel’s enthusiast desktop market has been waiting for an update for a couple of generations, and while the new 11th Gen Core Rocket Lake - S doesn’t migrate off of the 14 nm process node, we are at least getting a new microarchitecture that stands to deliver (according to Intel) a 19% IPC (Instructions Per Cycle) improvement. Intel lifted the lid a little on its next consumer flagship, the Core i9-11900K.
Rocket Lake - S is the processor that is plugging the gap while Intel continues to work on getting 10 nm ready for high-performance desktop use. Rocket Lake is built upon Cypress Cove, the reimagining of Sunny Cove that has been 'backported' to Intel's 14 nm process. The goal here was to enable Sunny Cove performance and instruction support, such as AVX-512 (Advanced Vector Extensions), a set of new instructions that can accelerate performance of microprocessor), on consumer 14 nm, albeit with the larger core size and any related power and efficiency changes. Rocket Lake also uses Intel’s new Xe Graphics, also re-designed for 14 nm. Intel saw fit to build Rocket Lake, which wasn't in its original plans, due to the delays on 10 nm, and now it seems ready to discuss its productization.
Another feature on the GPU side, along with enhanced performance moving to Xe graphics, is AV1 decode support, as well as always-on Quick Sync Video. With Rocket Lake, Intel is enabling both the integrated graphics and the discrete graphics to supply compute simultaneously, allowing users to enable their discrete graphics for gaming and the integrated graphics for stream encoding. This will be managed through additional software, such as that found on dual graphics laptops, that enable pointing specific software to different devices.
The new Core i9-11900K will also support DDR4-3200 as a standard (non-overclocked) memory speed, enabling Intel to reach parity with AMD, as well as 20 PCIe 4.0 lanes from the processor to supply bandwidth to a full GPU as well as a PCIe 4.0 x4 NVMe storage drive. Perhaps one of the biggest updates will be the connection to the chipset, with Intel doubling the DMI (Direct Media Interface) link from x4 to x8, doubling the total bandwidth available between devices connected to the chipset (like disk and SSD drives or networking) and the processor. Intel's DMI link is often equated to PCIe 3.0, which means we are at a PCIe 3.0 x8 equivalent link here. The chipset also gains support for USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 which is a 20 Gbps connectivity speed.
|
| Figure 3.5.51 Intel's microprocessor technology development. |
To the right of the figure, a section of the silicon wafer of the microprocessor is shown. It is simply amazing how many layers containing the circuit board to be done by all logic operations required for operation of the final product. There aren't even so many 'hamburger' layers.
| Intel® Z590 Chipset | |
| Essentials | |
| Product Collection | Intel® 500 Series Desktop Chipsets |
| Code Name | Products formerly Rocket Lake |
| Vertical Segment | Desktop |
| Bus Speed | 8 GT/s |
| TDP | 6 W |
| Supports Overclocking | Yes |
| Use Conditions | PC / Client / Tablet |
| CPU support | Comet Lake - S / Rocket Lake |
| Supplemental Information | |
| # M.2 Storage slots | 2 |
| Embedded Options Available | No |
| Memory Specifications | |
| # of DIMMs per channel | 2 |
| Processor Graphics | |
| # of Displays Supported | 3 |
| PCI Express Revision | 3.0 |
| PCI Express Configurations | x1, x2, x4 |
| Max # of PCI Express Lanes | 24 |
| I/O Specifications | |
| # of USB Ports | 14 |
| USB Configuration |
- Up to 3 USB 3.2 Gen 2x2 (20Gb/s) Ports - Up to 10 USB 3.2 Gen 2x1 (10Gb/s) Ports - Up to 10 USB 3.2 Gen 1x1 (5Gb/s) Ports 14 USB 2.0 Ports |
| USB Revision | 3.2 / 2.0 |
| Max # of SATA 6.0 Gb/s Ports | 6 |
| RAID Configuration | 0, 1, 5, 10 (SATA) |
| Integrated LAN | Integrated MAC (Intel Gigabit Ethernet) |
| Integrated Wireless | Intel® Wi‑Fi 6 AX201 |
| Supported Processor PCI Express Port Configurations | 1x16+1x4 or 2x8+1x4 or 1x8+3x4 |
| Package Specifications | |
| Package Size | 25 mm x 24 mm |
| Lithography | 14 nm |
| Advanced Technologies | |
| Intel® Optane™ Memory Supported | Yes |
| Intel vPro® Platform Eligibility | No |
| Intel® ME Firmware Version | 15 |
| Intel® HD Audio Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Rapid Storage Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Rapid Storage Technology enterprise | No |
| Intel® Smart Sound Technology | Yes |
| Intel® Platform Trust Technology (Intel® PTT) | Yes |
| Security & Reliability | |
| Intel® Trusted Execution Technology | No |
| Intel® Boot Guard | Yes |
Along with the new set of processors, motherboard vendors will be launching a variety of 500-series chipset based motherboards for Rocket Lake, and these motherboards will also support current generation Comet Lake processors. These new chipsets have an x8 DMI link to the CPU, unless a Comet Lake chip is installed, then it is only x4. Similarly, Rocket Lake will also work in 400-series chipsets, and the Z490 motherboards that are advertised with PCIe 4.0 support should have this enabled through a BIOS update. But Rocket Lake will not work with H410 and B460 chipsets.
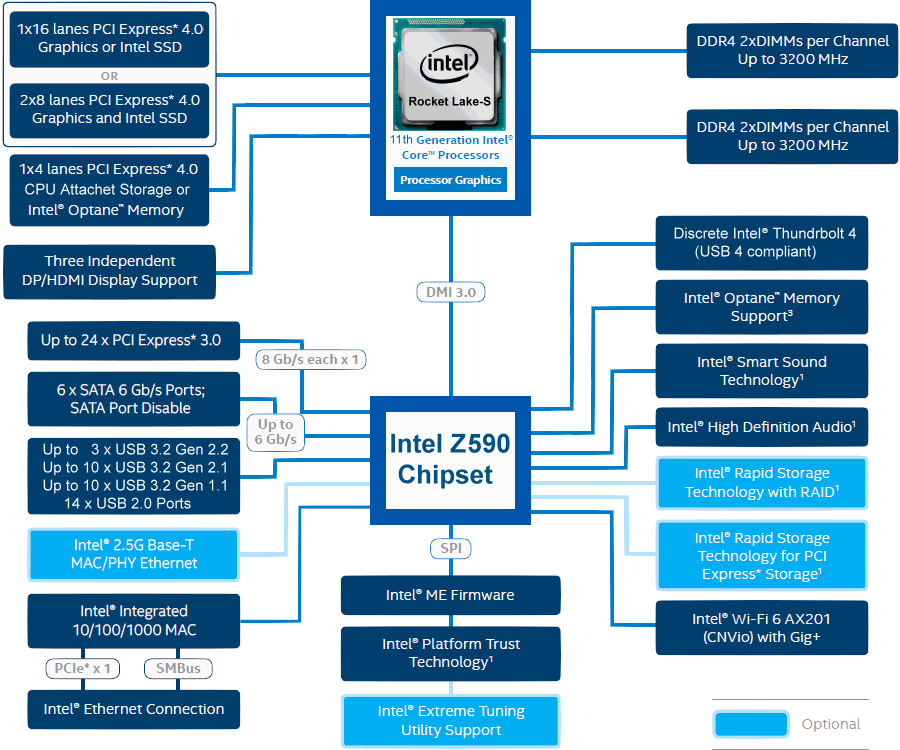
|
| Figure 3.5.52 Block schema of chipset z590. |
It's almost unbelievable that everything supports the z590 chipset. There is almost no need for additional devices, which is essentially the essence for the new generation of laptops. If the laptop doesn't have an optical drive, it needs almost nothing but an 11th generation microprocessor, a z590 chipset and a couple of matching M2 devices. In my opinion, Intel has done an excellent job with microprocessors and chipset for laptops, and I expect that the final product for PCs will be in the same range.
According to the description of motherboard classes at the beginning of this page, I chose to describe the MSI motherboard 'MPG Z590 GAMING FORCE' without Wi‑Fi support, shown in the following Figure. Of the seven possible slots for the ATX motherboard format, this motherboard supports five that are fully usable using a single graphics card in the first slot. Other unused slots can be used, for example, to install a TV card, Sound card, Video Capture Card, ADA metering system or some other specialized card.
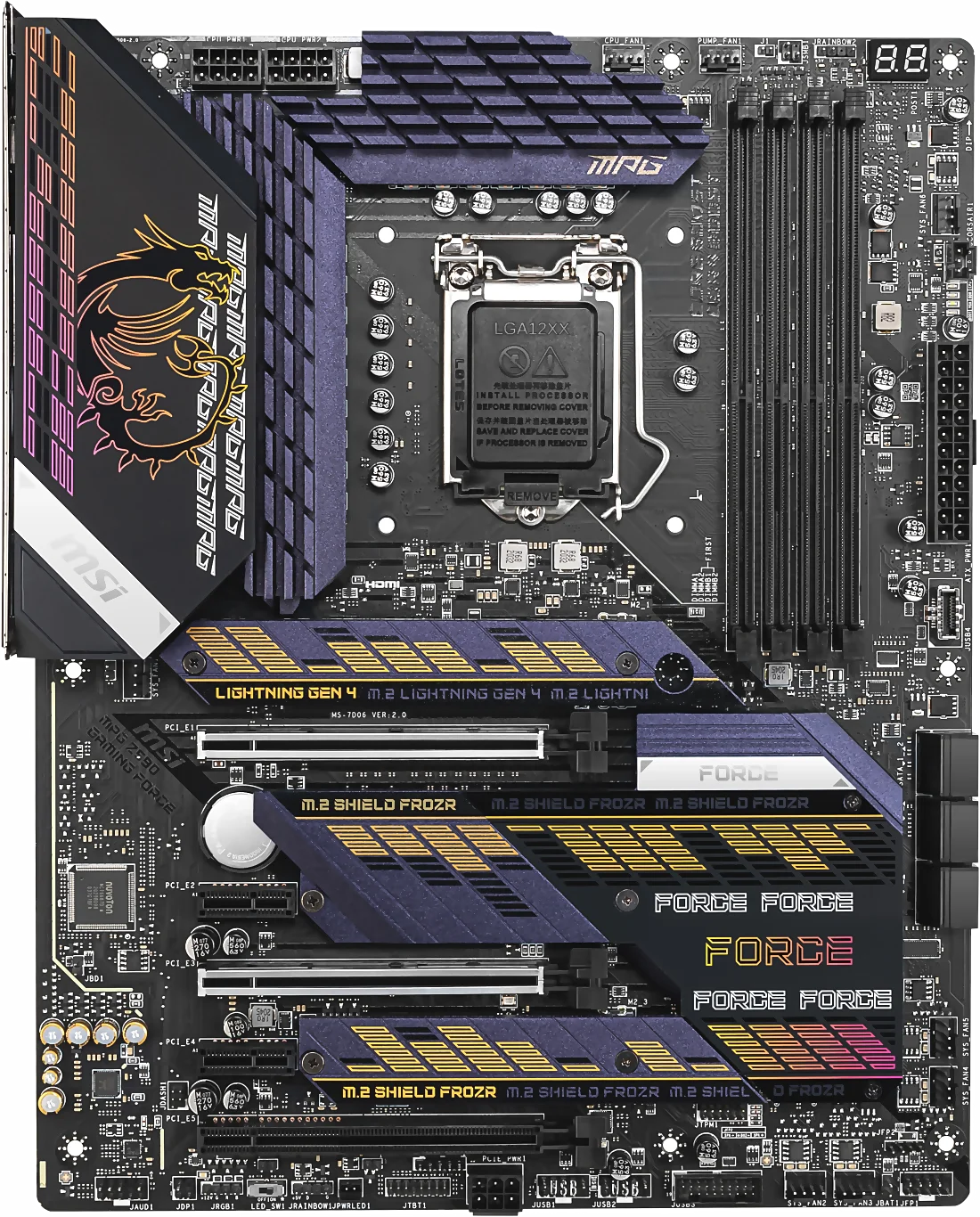

|
| Figure* 3.5.53 MSI 'MPG Z590 GAMING FORCE' motherboard. ( + / - ) |
The motherboard uses three full-length PCIe slots, with the top two operating at PCIe 4.0 x16 or x8/x8, and the third one operating at PCIe 3.0 x4, with two additional PCIe 3.0 x1 slots. Looking at storage options, it includes one PCIe 4.0 x4 M.2 slot, with two PCIe 3.0 x4/SATA M.2 slots, each of them covered by its own fancy purple and yellow accented heatsink. The board also includes six SATA ports with support for RAID 0, 1, 5, and 10. Located along the bottom of the PCB is a 6-pin 12 V GPU power input, which is designed to provide more power to the PCIe slots, although this is a very niche inclusion and is not entirely necessary.
The capabilities of this motherboard are best described by the block diagram in Figure 3.5.53b. The Figure shows this better than some super-expert description. Motherboard connectors are shown in the following Figure and their number can be easily increased using dedicated brackets and connectors at the motherboard.

|
|
| Figure 3.5.54 Connectors at 'MPG Z590 GAMING FORCE' motherboard. |
The motherboard 'MPG Z590 GAMING FORCE' really provides versatility in its use, and although it belongs to some middle category of motherboards it is quite expensive. A popular proverb says, 'Pay, and mock.'.
SUMMARY:
I like this motherboard although it will not be in use for a long time. Namely, Intel intends to switch from LGA 1200 to LGA 1700 socket for the next generation of microprocessors, and that would be the Alder Lake - S platform, which in addition to a new socket will bring a new rectangular format for the processors. Rumors say that the purpose of this rectangular design and the rather massive number of pins are most likely due to a design change towards a multi-die design, housing two DIEs at 10 nm to compete better with the AMD platform. We'll see.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |