TCP / IP network settings |
In the previous Chapter it was emphasized that the network diagram two computers can have the same name. The same applies to IP addresses. If there is a 'conflict of interest', followed by conflicting messages on the computer desktop, which can not be permanently excluded. IP is an integral part of the Internet Protocol and is set in the card ||General|| when setting the properties of the network card. If a network card is meant primarily to wire network of an institution, company or corporation, though, and wireless communication can similarly set but with the additional safety protocols.
|
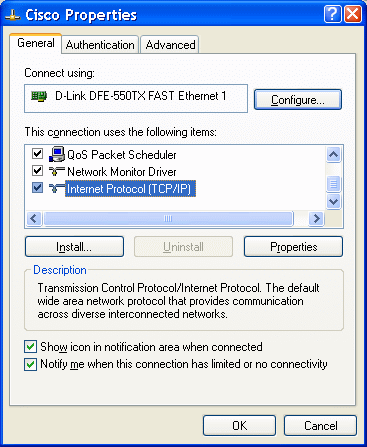
| Figure 4.4.31 The choice of network protocol. |
It is useful to include the option in the boxes so that the network card icon always present in 'tray' part of the menu system. If there is no network cable icon is crossed out, and if the network cable is there but there is no communication icon is faded, if it is a fine position the mouse cursor on the 'pop' window with the basic parameters of the connection. Very handy for quick diagnostics.
When selecting a protocol (could be installed IPX / SPX would very Novell supporters rejoiced, but viruses and worms would not have), via options |Properties| follows input form parameters as shown below.

|
| Figure* 4.4.32 Set the TCP / IP protocol. ( + / - ) |
It has already been noted that the parameters of the network card configured through the {Administrative Tools}, type of traffic, speed, and more. IP address shown in the Figure, are entered based on the already established network schemes, as the example in Figure 4.4.32a, or SOHO device obtain the required parameters if the network settings is according to Figure 4.4.32b. In the example of Figure 4.4.32a according to the private network to the ' B ' class (more on this in Chapter 7.4.4), which is access to the Internet (gateway) IP address of the Ethernet port router or network card dedicated servers, and DNS address and electronic mail services, web sites and the like are on another server, which allow public access. In this way, members of 'invisible' to the Internet and is the only publicly available e-mail and web server, along with additional services (services) that will accompany it.
Very interesting choice of cards is shown in Figure 4.4.32b called ||Alternate configuration||. It automatically appears when the card ||General|| selected to the TCP / IP settings automatically set (choice |Obtain an IP address automatically| and |Obtain DNS server automatically|) if there is an active network DHCP services, such as case with SOHO devices. Corporate networks, usually wired, usually do not have the service active. If you have an active DHCP service, then it is a separate wireless network for general use. Then, for example, the laptop can be configured with the parameters in the card image 4.4.32 ||General|| be set to automatic adjustment in respect of the reach of wireless networks, and the parameters Cards ||Alternate configuration|| that contain data for a wired network.
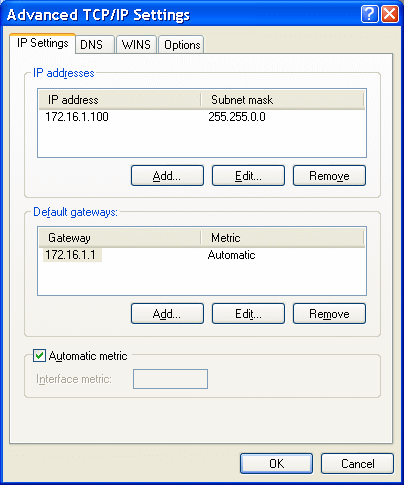
The next card is obtained by choosing |Advanced...| from the previous picture, confirming entered parameters, and Figure 4.4.32b shows how to define the WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) cares about traffic when a Windows server. It is a service that allows you to build a dynamic table that corresponds between host names and their IP addresses if they are members of the network can easily identify. So records are not permanently recorded, but are dynamically updated so that the computers in the network involved.
|
| Figure* 4.4.33 Advanced TCP / IP settings. ( + / - ) |
Example I
Computers are in the same network.
Are set so that they have the same workgroup, network mask, and part of the IP address that the network mask 'hold'.
All computers have different names and different IP addresses. Have the same network mask, and belong to the same network and the same workgroup. Sharing the first two numbers of the IP address that corresponds to the number of network masks '255,255'. Netmask, when using the marginal address class can only have the numbers '0' and '255' and the IP address of the computer may not have listed numbers. IP address where it is the network mask '0', has the number '0' represents the IP address of the network - NETWORK (172.16.0.0), and if the IP address to a specified place instead of the number '0' number '255' to IP ADDRESS OF ADVERTISING - BROADCAST (172.16.255.255), which is published by the presence of the device on the network and the availability of shared network resources. For computers are said to belong to the network in the ' B ' class. According to the example it can be calculated that this network can be 254×254=64'516 computers to see each other. Small distribution can be made by changing the name of the working group, but it does not contribute much delimitation.
In addition to network addresses and the addresses of advertising on the network is always defined by one address for the computer output from the network, typically address ethernet port on the router and is called GATEWAY. Advertising mechanism when one IP address sends a user group called multicast and it's uniqueness of ' D ' class, which combines network and active network equipment and enables communication between devices active network equipment. The address is one computer in a network is called a unicast address. Computers in the network communicate with each other by means of active network equipment recognizing unicast addresses.
Example II
Set up your computer from the Example I in the two subnetworks.
Third and fourth examples of the computer and changed the corresponding working group and network mask everyone is set to the value '255.255.255.0'. Changing network masks some computers have become members of separate networks ' C ' class, which in this case subnet existing ' B ' class. Due to the different number of network masks third group ST computers are not in the same subnet with computers ZG Group. Some groups of computers are not advertised to the same addresses and can not see each other. According to this conception were found 254 subnets, each with 254 computers. Dividing the network into smaller subnets (subnetting) within a larger network is performed in order to better control network traffic, better security and smaller amounts of advertising in the subnet. Sharing network class ' C ' in smaller portions shown in Chapter 4.5.5.
In the example I and II all computers can connect to the same active network equipment without the need to define virtual networks (VLAN). The term 'computer' thought generally to a device that has a network card, and defined an IP address, so the server, network printer, copier or projector with network capabilities, or whatever.
Example III
Connect two computers without an active network equipment.
This means that the two NICs directly connected. This in turn means that transmitting traffic for a network card should be on the receiving part of the second network card. Then the standard cable for connecting the device to be replaced with a CROSSOVER which has a 'crossover' pins on the RJ45 connectors. Computers must be in the same network and the same workgroup but different names and IP addresses.
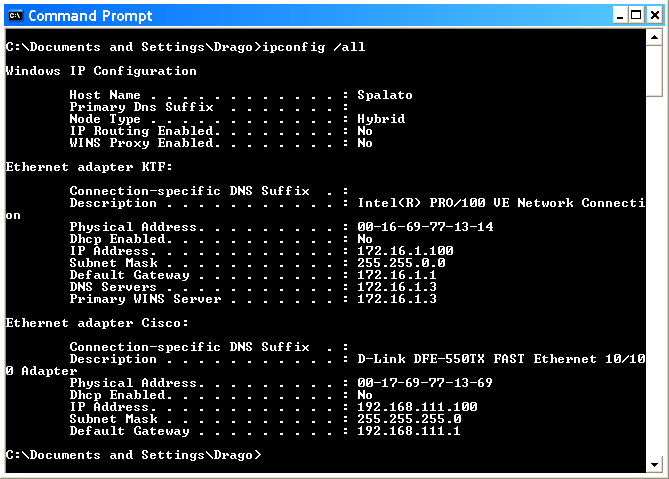
When everything previously stated it is useful to make a quick check to see if it all fits together well done. Unavoidable use CMD and command IPconfig /all gives a detailed account of a curious system engineers.
|
| Figure 4.4.34 View of network settings via the command window. |
What is of great benefit to the physical address of a PC (Physical Address), which is basically a binary notation addresses of the network card (MAC address) is a 48 bits (12 hexadecimal numbers), of which the first group of 24 bits is the code producers, the other serial number of the network card. Basically there are two network cards with the same number, which is very useful when one wants to increase the level of safety, if the switch allows it to be defined in some of his port can only work with the default computer MAC address. Not that the MAC can not be faked, but you can not know what is written in the switch. This record is a nice save to disk (IPConfig /All >A:\spalato.txt) or on a USB stick, printed and go to the archive system engineers.
SUMMARY:
Thus, network mask ' B ' class is 255.255.0.0. But if, within the ' B ' class network mask using ' C ' class, 255.255.255.0, it is possible to separate the computers into smaller interest groups, which reduces the amount of advertising and the response to the network when traffic between the participants, and the group itself seems invisible to each other. With a network mask ' C ' class can be defined subnet 254 that they do not see each other. On selecting a different network masks can be obtained with a smaller number of subnets multiple computers within the subnet, or vice versa.
Specified IP address from the examples belong to the private address of the network. It means that you router (router) does not fail to public content online, and within the network must be a device that will conduct 'translating' private addresses to the public. It usually works a router or a dedicated server. In computer world this address translation mechanism is called NAT (Network Address Translation), and is also known as the 'network masking' or 'IP masking' (masquerading).
In practice, the above means that computer within the network if 'wants to get out there' contacting the server through one network card (internal traffic) accepts the request and over the second network card fails ga towards a certain goal (external traffic) by giving to the unique server IP address. In doing so, the server creates a table in which it is written that belongs to the internal IP address of the network. In this way the 'famous outer' and 'inner-known protagonist of the Internet to communicate, but only at the initiative of the' internal 'network. Other participants in the Internet can see this only as a link connection external participants and servers. Thus, it can be realized only traffic that is initiated by the participants 'internal network' while the reverse is not possible. This is a common mechanism to increase safety and extend the range of available IP addresses within an institution or firm. Services that must be available to the public, such as email or web content, must be on the servers that have public IP addresses. The network card configuration server gateway address is the IP address of the network card that receives traffic from the inside to the outside, and the IP address of the second network card that connects the server to the Internet, one of the public address facilities.
And when it all falls into place by the two above examples, there is still some 'little things' that need to be done to your computer to the Internet improved their connectivity as setting the number of concurrent connections to other users on the network, set the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) - Size data packets and the like. It is desirable for this purpose, read the contents of pages of type 'Windows Tips and Tricks', and the simplest is to use the free tool 'SG TCP Optimizer' that can be downloaded by following the hyphen. Setting up the registry and use this tool means you must know how to do at least some basic 'interventions' in the registry or simply use the default option ||General Settings||-|Optimal settings| this tool.
But when everything is put in its listed address as shown in the example, it does not mean that the networking and sharing of resources possible. Should check that your firewall allows communication between computers. The firewall needs to allow sharing of resources and determine which IP addresses or their range, as well as the port's, firewall miss. A little more complicated if computers use ADSL router (and switches) when the IP address changes automatically every few hours (DHCP). Then you have to miss the address range that serves the computer, which can be inconvenient because they are visible and other computer users who are in the same range of addresses. Then you have to right to shared resources assigned directly to users, which means that for example three users in the network, each of which has its own computer, every computer should have a user name of each of them, and users with the same name to be opened on any computer, and rights to resources to enable them only in the image 4.4.9 of the card over ||security||. More on the firewall on.
In the end, it is possible to conclude that the matter on the same network computer must have a different name and different IP address, and the name of any user's computer may not be the same as the name used by the computer. True Windows XP installation procedure will not allow it, but Windows 2K will. So, when planning a user name, computer name and the address of the said scheme should take care.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |