Ethernet network card (NIC) |
 NIC (Network Interface Card) or, also called a LAN adapter, crucial and the starting point of any network communications. In choosing to follow its protocols (Ethernet / Token-passing / FDDI) and media type (Twisted Pair / Coacs / wireless / fiber-optic). Once it is so popular 'Combo' network card, shown in Figure 3.6.17, which enabled three ways of connecting to the network, of course, with the use of only one of the available modes of communication with the network infrastructure. Network card has a unique code called a MAC (Media Access Control). This is a binary number of 48 bits, which are often presented in hexadecimal form as PP-PP-PP-SS-SS-SS. The first 24 bits (PP ...) marks the manufacturer, and the next 24 bits (SS ...) belong to the serial number of the card. As directed by ISO can be no more cards with the same serial number, which means that the MAC address is unique. There is a PC, network printer, Ethernet port of routers and similar devices. It belongs to the devices of the second layer of the OSI model what it means to know what to do with a FRAME. In the following figure shows the block diagram of communication two network cards.
NIC (Network Interface Card) or, also called a LAN adapter, crucial and the starting point of any network communications. In choosing to follow its protocols (Ethernet / Token-passing / FDDI) and media type (Twisted Pair / Coacs / wireless / fiber-optic). Once it is so popular 'Combo' network card, shown in Figure 3.6.17, which enabled three ways of connecting to the network, of course, with the use of only one of the available modes of communication with the network infrastructure. Network card has a unique code called a MAC (Media Access Control). This is a binary number of 48 bits, which are often presented in hexadecimal form as PP-PP-PP-SS-SS-SS. The first 24 bits (PP ...) marks the manufacturer, and the next 24 bits (SS ...) belong to the serial number of the card. As directed by ISO can be no more cards with the same serial number, which means that the MAC address is unique. There is a PC, network printer, Ethernet port of routers and similar devices. It belongs to the devices of the second layer of the OSI model what it means to know what to do with a FRAME. In the following figure shows the block diagram of communication two network cards.

| |
| Figure 7.4.9 Block diagram of Ethernet network cards. |
Originally Ethernet is half-duplex technology. NIC can transmit and receive data simultaneously. NIC checks for signals on the 'wire' it sends its own. That's why it needs the collision detector. If the 'wires' for any reason busy broadcasting is delayed. If two NIC broadcast simultaneously result of a collision signal on the 'wire' and they will be counted and this increase voltage signal indicates a collision. NIC which was first established collision sends JAM signal (a particular sequence of bits) as the order to the rest of to stop broadcasting. When the broadcast ended, each card will help you 'back-off' algorithm to calculate how long it will try again to start broadcasting. This time is calculated by a random process and is not the same for each NIC. When all become silent first NIC which expires this time will begin broadcasting. If its signal reached the other NIC and that they are not emitted will continue normal transmission, while others will wait until the end. This is the principle of CSMA / CD and about caring Ethernet controller. Collision is normal. Loopback is used for internal verification function when the NIC itself sends FRAME. What's more NIC's ability to collisions on the network grows, and a strong network traffic can lead to a large number of collisions and thus repeat broadcasts, which significantly reduces the efficiency and throughput of the network. As NIC has a lot to do well as far as possible standardized card type to be used.
But Mac address not apply to you only to your network card usually recognize the PC as an electronic circuit that is inserted into a PCI slot. There is every device that accesses the Ethernet. Thus, for example, each Ethernet switch port or router will have its MAC address. Demanding printers or copiers may contain electronic modules with built-in networking and its unique MAC address, and thus they become participants in the network traffic. When so many of the network should mention something network scheme that is used in the Internet world. IP is the basis of recognition of computers in the network and it is a 32-bit track that is divided into 4 groups of eight bits, and is presented as a hex notation HH-HH-HH-HH, (digit H = 0-F) or more frequently as the corresponding the decade numbers separated by a period as DDD.DDD.DDD.DDD (number of DDD = 0-255). This address type is described by four 'DOT' decade figures called IPv4.
The presented scheme is in principle applicable to the network card for wired communication. For wireless communication concept receivers and transmitters to expand the system for receiving and transmitting electromagnetic waves, and a system for encrypting and decrypting for security, both in terms of access to the system as well as with regard to access to the content.
IP address of computer or network device contains two important pieces of information:
ISO has defined several classes of PUBLIC and PRIVATE networks specifically to NETWORK and HOST share the IP address as follows:
Class A - N.h.h.h with network mask M.0.0.0 1-126.h.h.h (IP/ 8)
Class B - N.N.h.h with network mask M.M.0.0 128-191.N.h.h (IP/16)
Class C - N.N.N.h with network mask M.M.M.0 192-223.N.N.h (IP/24)
Class D - N.n.n.n doesn't have (multicast) 224-239.n.n.n (IP/32)
Class E - N.n.n.n doesn't have (reserved) 240-255.n.n.n (IP/32)
Class A 10.000.000.000 - 10.0hh.hhh.hhh with network mask M.0.0.0
Class B 172.016.000.000 - 172.031.hhh.hhh with network mask M.M.0.0
Class C 192.168.000.000 - 192.168.255.hhh with network mask M.M.M.0
By default, communication between a private and a public network is only possible if the call was made to a public network from a private network, because the gateway does not allow 'intrusion' into the private network from the public network.
'N' and 'h' are the the decade number in the range 0-255, where the '0' and '255' are reserved for special purposes. If the all host portion contains '0' that is IP address of the network. If the all host portion contains '1' that is the broadcast IP network address (advertising address). So, part of the host that is available to a computer or network device to identify them in the network are binary equivalents by decade numbers from 1-254. So are certain classes assigned specific numeric ranges that relate to public addresses or private addresses used by an organization protected by a firewall. 'M' is everywhere 255 when the networks are not divided into smaller subnets, and is an integral part of the network mask, which task is to allow multiple local computers and internal subnets which the Internet 'see' as one unit, or as a single path or arrival departure of the data between the Internet and a local area network (LAN). IP_address / number belongs CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) notification that indicates how bits from the left IP addresses makes network address. CIDR notification allows the network that are not in the strict frames the class boundaries, for example IP/13.
Each of the classes of network addresses can be divided into internal SUBNETWORKS so that some bits of the 'h' portion to take advantage of the subnet, and so local network is divided into multiple independent parts. Then it changes the value of 'M' in the section that defines how the HOST part taken for the subnet. To know how many bits of the IP address refers to the network of computers and how to define the network mask where the network bits are '1' and '0' are computer bits. When you perform a logical AND operation between the IP address and NETWORK MASK derived from the NETWORK ADDRESS (NETWORK ID).
IP address
AND
Network mask
---------------
Network address
Example of division the network of class ' B ' in the subnets of class ' C ', on the class boundaries, is given in Chapter 4.4.4, and the example of division the network class ' C ' is given in Chapter 4.5.5. When division of the network (subnetting) carries out boundaries, it is useful to address computer and network mask into binary code and then execute the division, in order to reduce the possibility of error in calculation, or create the appropriate table as the page about the CLI commands of the operating system at Cisco network devices.
As part of the internal subnets internal network device that diverted traffic between networks (routers) are used exclusively by analyzing the network address using a netmask. So that they can 'get' the network must know the IP address of the router and these three data are entered into the computer like this:
CFomputer IP address : 201.253.132.7
Network mask : 255.255.255.0
Default 'Gateway': 201.253.132.1 (Router IP address)
IP address of computers or network devices in the network of the example, it can be set in the range of 201.253.132.2 to 201.253.132.254. Based on the network mask and IP address of any computer calculates the network address, which always ends with '0'. To advertise (broadcast) serves the last IP address in the whole range which in this case means that it ends with '255 '.
Network IP address : 201.253.132.0
Broadcast IP address : 201.253.132.255
Network in which the computer and network devices recognize each other is called the broadcast domain (advertising) in which computers and network devices after initial connection communicate directly using the physical (MAC) addresses.
So, according to the example, a computer with a number '7 'communicates with the interface '1' regarding traffic to the Internet, and the network to which the computer belongs to a class ' C '. As computers for some services using their name and the domain to which it belongs, which is more easily remembered than tedious numbers of IP addresses, one of the server in network provides the service of translating the IP addresses and names - DNS (Domain Name Service), and vice versa, and it is specified IP address of the DNS server.
Address of DNS server : 201.253.132.2
So this is a special computer with other computers on the task of providing the necessary services, such as DNS services listed. In its DNS tables inscribed interdependence exists for example:
computer.domain.country <-------------> IP address of computer
(mare.spalato.hr <-------------> 192.168.255.7)
In addition to the DNS service that computer (server) can provide the service of electronic mail and the WWW, or all services will be performed with a number of separate servers. And to servers and computers in the network is assigned name and IP address within the range of classes they belong to, and should not exist in the network multiple computers with the same name or IP address. Traffic on the local network is conducted by identifying the MAC address of individual computers, and the traffic outside the network is carried out by finding the IP address of the destination computer somewhere on the Internet.
DNS services for individual computers makes sense when wants to include computers in the public with computer constantly - STATIC IP address and host names. A static (fixed) IP address is of great importance for servers that must be available at all time, because of their name or their IP through DNS to direct all requests to available services, and if they provide citizens with an IP address must be stated publicly. For individual users on the network is not of significance fixed IP address, it is best to focus on the DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) service, which enables the IP address changes periodically, or the user of a computer when you connect to the network assigns the first free address within the defined DHCP range in class. This service is very useful when you have multiple computers that occasional use of the available network services address class to which they belong (laptops for example).
A better solution than this is NAT (Network Address Translation). All computers are defined in a private class addresses that service NAT server, router or firewall which translates all private computer addresses into a single public address and thus computers inside a private class makes it invisible to the public. The servers can remain part of the network that is visible from the outside, but then unprotected. One can choose a private class address at will, depending on the number of computers that needs servicing. If you are in a private network and provide DHCP services for the 'guests' and servers within a network is important for the public on make direct translation of public and fixed IP address with traffic control for them, the result is a very secure and flexible organization computer networks on share publicly available and hidden (differentiation network). So, there is static NAT (SNAT) and dynamic (DNAT) elements, and the network is divided into protected and unprotected but controlled area. Unprotected controlled area commonly referred to as a demilitarized zone (DMZ - demilitarized zone), and unprotected area outside the private network is called and doubtful (bastion hosts).
NAT and DHCP can be implemented using a server with two network cards and software that basically have all the Windows or Unix servers, a router with a built-mentioned characteristics or dedicated firewall, depending on what each of the devices can be and how much money. Firewall as a separate device is good but expensive solution. NAT is also a network of protection from external attacks of any kind (DoS, worms ...) because the computers inside a private network invisible. How, then, establishes communication? Simply, it works only communication that is initiated by the user in the private network. This means that for example a program for remote computer (such as VNC software) that is located in a private network will not work if the connection is not initiated by the user in a private network. External users can not initiate a connection because 'knows' how to get to a computer in a private network. This can make it difficult or completely disallowing P2P software (Hu!). What if the firewall is canceled? Should endeavor to repair and wait or networked TWO!
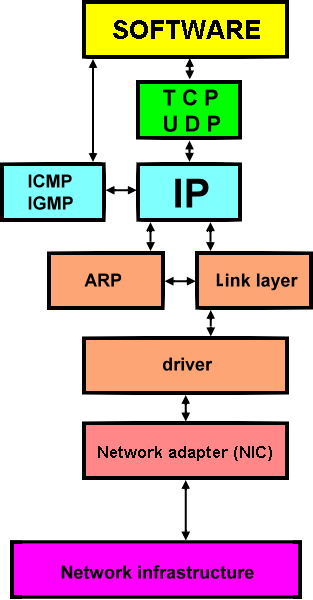
Network adapter, regardless of physical and electronic version (PCI, USB, wireless ...), the basic hardware component that allows the computer to communicate with the network infrastructure. The computer recognizes it on the basis of installed DRIVERS whose task is to achieve a successful communication between the network adapter and operating system. Drivers are supplied with network adapter in a convenient storage medium, usually a floppy disk or optical media, or are based on information written on the adapter (card manufacturer and type) to take them from the Internet, and by installing a network card in the computer follows installation of diver in the operating system of computer. Implemented network operating system protocols allow further exchange of data to the appropriate software. Default set of protocols for computers in the network is TCP / IP, although it can be implemented and others like Novell NetWare IPX / SPX. The following figure shows the principle use of the TCP / IP stack of protocols in the computer.
 |
|
| Figure 7.4.10 Network communication in the computer. |
Network adapter has its own MAC address that he used to communicate with the network device with which it is connected via communication lines, and the table in Chapter 7.4.3, for exchanging data FRAMES between the network adapter and network devices based on the identification of the destination and source MAC addresses. Depending on the direction of communication depends on where it will be the MAC address of a network adapter. All network devices, including the computer, using the ARP protocol (Address Resolution Protocol) to achieve initial communication between physically connected devices and comprehend to whom the communication relates. FRAME contains data that accepts network adapter or device that applies from the data extracted and unpacked - decapsulating data processed by the superior protocols (IP, ICMP, TCP, UDP ...) which are taken from the PACKAGE in FRAME and contains the source and destination IP address, from which it then allocates segment that monitors the correctness of delivered DATA program support. For the same purpose may be used program support (software) from different manufacturers that are basically installed in the same way as the network adapter drivers of operating system. Network communication has already been described in detail through the OSI model shown in Figure 7.4.6, a special chapter deals with the TCP / IP protocols.
Based on the above it is clear that if there is no communication without respect RECOMMENDED communication standards. Who do not comply can not communicate, the choice is on his willingness. So, basically there is no imposition, but the recommendations are clear and available.
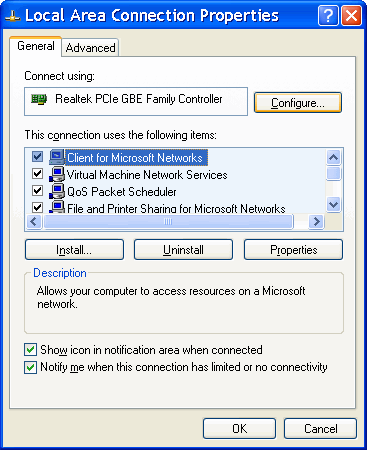
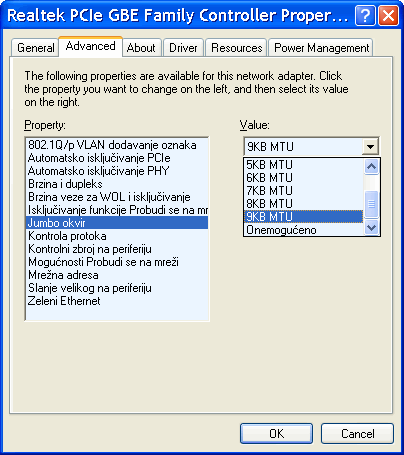
Each network card will be automatically configured according to the default settings that can be changed for each of the parameters according to Figure 7.4.11, the choice |Configure...| and settings on the card ||Advanced|| according to Figure 7.4.12.
 |
| |
| Figure* 7.4.11 Choice of Configuration NIC | Figure* 7.4.12 Operating parameters of NIC |
Depending on the quality of control program (driver) depends on the number of parameters that can be adjusted so that the display in Figure 7.4.12 is not an established rule. The Figure shows the MTU setting for 'Jumbo Frame' if the computer is connected to the multimedia switch.
SUMMARY:
The rapid growth of the Internet has led to the problem of 'free' IP addresses. Namely, as already introduced IP telephony and a large number of firms are intensely informatize, lack of IP addresses is a growing problem. Therefore, the standard expanded to an IP address has 128 bits. Designation of this standard and its IPv6 header is shown in the following table.
| 4 | 8 | 16 | 24 | 32 |
| Ver. | Priority | Flow label | ||
| Payload length | Next header | Hop limit | ||
| -- Source address (128 Bites) -- | ||||
| -- Destination address (128 bites) -- |
||||
| Structure of the IPv6 header in 32 bit lines. | ||||
The basic header is pretty simplistic. Field 'Next Header' indicates the addition of header immediately following this header and the next header may be more a qualitative shift in relation to the IPv4 standard. IP address is displayed of hexadecimal 8 groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by a colon with the leading '0' of groups do not have to write. The following is the general form and two examples of IPv6 addresses.
HHHH : HHHH : HHHH : HHHH : HHHH : HHHH : HHHH : HHHH 1080 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 8 : 800 : 200C : 417A FF01 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 0 : 101
Are supported network cards and operating systems IPv6 protocol? All newer network cards from the era of the operating system 'Windows XP (SP3)' onwards, their drivers as well as operating systems support both protocols, but must choose a protocol that will use the system. Simultaneous use of both types of protocols is not usually possible, but only through the use of tunneling with the appropriate program support.
Realized that the computer access to the Internet? Windows XP/Vista/7 a PING command that operates on layer 3 of the OSI model and it can be a very quick check of networking. Is named according the SONAR system, which works on the principle of sending sound pulses through the water and measuring the echo time.
Internal check of NIC : PING 127.0.0.1 (IP address of 'loopback' test) Checking PC configuration : PING rrr.rrr.rrr.rrr (IP address of computer) Checking network output : PING ggg.ggg.ggg.ggg (IP address of router / gateway) Checking destination : PING ooo.ooo.ooo.ooo (IP address of destination) C:\>ping 74.86.121.4
or
C:\>ping buzdo.com
if the domain is recognizable through a DNS server. Pinging 74.86.121.4 with 32 bytes of data: Reply from 74.86.121.4: bytes=32 time=187ms TTL=48 Reply from 74.86.121.4: bytes=32 time=188ms TTL=48 Reply from 74.86.121.4: bytes=32 time=190ms TTL=48 Reply from 74.86.121.4: bytes=32 time=188ms TTL=48 Ping statistics for 74.86.121.4: Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 187ms, Maximum = 190ms, Average = 188ms C:\>
There is also a command TRACERT, program used for monitoring a connection to the destination.
C:\>tracert buzdo.com Tracing route to buzdo.com [74.86.121.4] over a maximum of 30 hops: 1 29 ms 28 ms 30 ms 193.198.190.157 2 28 ms 30 ms 28 ms CN-Srce-02-ES.zg.core.CARNet.hr [193.198.228.129] 3 29 ms 29 ms 28 ms CN-Srce.01-RO.zg.core.CARNet.hr [193.198.228.21] 4 50 ms 38 ms 38 ms carnet.rt1.vie.at.geant2.net [62.40.124.9] 5 38 ms 37 ms 38 ms tenGigabitEthernet1-3.ar2.VIE1.gblx.net [64.214.145.145] 6 180 ms 180 ms 181 ms te1-1.cer03.dal01.dallas-datacenter.com [64.215.81.2] 7 181 ms * * po3.dar02.dal01.dallas-datacenter.com [66.228.118.211] 8 182 ms 182 ms 180 ms po2.fcr03.dal01.dallas-datacenter.com [66.228.118.190] 9 185 ms 181 ms 182 ms cms.wmd-linux.com [74.86.121.4] Trace complete. C:\>
Small curiosity: If a 'bad system' to intercept the communication between the end user and his server, acting as a server interface can fool the user in a way that the user thinks he has merged with his server (in the bank!), It is possible to abuse the user's data. Thus, in addition to one-time use password encryption access and synchronization mechanism watches user's computer and the server, and if the difference in time transmitting and receiving packets larger than a couple of seconds, the server will interpret it as a fake traffic and refuse to communicate. Encrypting traffic and increasing investment in security mechanisms is a feature of today's computer networks.
How many computers with Windows XP/Vista/7 operating system to connect to the network and a small introduction to the planning of the network IP address scheme is shown in Chapter 4.4.4, indicating that directly connect two computers NIC-to-NIC without an active network equipment using a crossover cable. In Chapter 7.6. shown is a device that combines the basic functions of professional networking devices for small business or home environment - SOHO (Small Office / Home Office). In the example in Figure 4.4.16 shows how to assign addresses to computers and devices in a private home network (SOHO) in a private class ' C '. How private address network devices do not leak, SOHO device must have the ability to transform the private address using a combination of addresses assigned by the ISP and the port (Figure 7.6.9) with respect to the contents out of the reach of home network.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |