4.4.9. RAM-Disk |
If part of physical RAM to declare 'hard disk' the software that it provides during the boot process, the operating system, there's a memory device data according to the principles of the hard drive is much faster than physical hard disk and is called a RAM-DISK (RD onwards). Working memory access time is measured in ' ns ' of access time while the hard drive access time is measured in ' ms ', and the obvious advantages of RD.
RAM disk is used already, the basic idea was to use the working memory that CPU can address a device similar to disk as the physical disk drives were slow and expensive. It can be a dedicated programming support within the operating system to create and use, for example CP / M and MS-DOS operating systems, and can also be used in modern operating systems. But some of these great benefits if no amount of physical RAM small and if used right its available and visible part of this purpose, it will 'strangle' performance of the system as a whole. Therefore, the described concept is not gladly used in normal computer operation. Ware system that runs from a CD or similar devices, type 'BartPE' or antivirus program running on a manufacturer's or CD contents to the regeneration of damaged operating system used with RD to copy some content to it and run them and that serves as a medium for recording and processing of data they are currently needed.
Windows XP in 32-bit version can address 4 GB of physical working memory of which for user is available around 3.25 GB while the rest of 'no see'. If you add more RAM the operating system is essentially of no benefit. With the advent of 64-bit operating systems has significantly increased address space to physical memory, but it can happen that some important 32 bit applications do not work properly. This may be the reason to install 32-bit operating system on a computer. Working memory is no longer a high price and all newer motherboards for home computers can recognize and use more than 4 GB of RAM which is specific CHIPSET, but 32-bit operating system for home / office computer with the provided not cope. As with the motherboard and modern microprocessors support 'expanded' 32-bit addressing to 36 bit, PAE - Physical Address Extension, handling with greater amounts of physical RAM is possible.
Thus, the chipset features PAE is the added ability with regard to enabling the microprocessor to work with more than 4 GB of physical memory. The following 32-bit operating systems use PAE to be able to work with more than 4 GB of physical memory:
|
Process running in the operating system can use up to 2 GB of memory address space (if not used switch /3GB). Part of the memory being physical memory and some being virtual. The more programs, thus increasing the number of processes requires more than 2 GB of address space. When this situation is aggravated by the use of virtual memory, which negatively affects the performance of the system. Therefore, servers and their operating systems uses PAE to ensure the availability of large amounts of physical memory that control access with 'memory manager' allocation of the PAE memory regardless of programs running. Chipset server computer is something quite different from the chipset of home / office computers, and servers and their 32-bit versions of the operating system capable of utilizing all of the above with the 'extended' addressing working memory.
Program support server must know how to use the resources offered to worry about is the AWE (Address Windowing Extensions), a set of application programming interfaces (Application Programming Interface - API) functions for which the memory manager makes use of more than 4 GB of memory that is available through standard 32 bit addressing through the dynamic memory mapping in the working set of memory, and thus systems with databases allows to reserve large amounts of physical memory for the data.
This list of operating systems is part of the explanation of the company's support pages to users 'Microsoft' and refers to the 32-bit versions of operating systems and can be concluded that the 32-bit versions of operating systems for home / office computer type Windows XP/Vista/7 not able to take advantage of memory resources as servers. Thus, information about the computer system essential to enable and use PAE are:
|
The order of importance of meeting the criteria in the order listed. If the chipset or CPU does not support the above (all modern microprocessors support) other factors are not significant. If the operating system supports PAE does not mean you will be automatically activated when using more than 4 GB of physical RAM. Core operating system to 'suggest' that all conditions are satisfied amendment arguments in the initial file. To enable PAE, use the /PAE switch in the Boot.ini file as follows:
[boot loader] timeout=30 default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS [operating systems] multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)\WINDOWS="Windows XP" /noexecute=optin /fastdetect /PAE
Of course, it is a 32 bit Windows XP operating system which is the subject of this Chapter. If your computer includes more than 4 GB of RAM, as in the following example uses 6 GB, one of the ways of utilization of surplus of working memory without switching to a 64 bit version of the operating system is just the use of RD in a way that serves the same working memory that the operating system 'sees'. All software for the creation of RD, especially free, no referred to, but the free version allows 'VSuite Ramdisk' that satisfies the basic purpose and commercially available are more efficient versions. The assumption of efficient use of this program is the active support PAE. After installing and running the downloaded program support is first set the parameters in the window according to Figure 4.4.57a.

|
| Figure** 4.4.57 Retrieve PAE memory / Create RAM disk device. ( +/- ) |
The Figure shows how the operating system 'sees' the total physical RAM and should be enabled to reach this program support choice ||Options||-|Enable OS Invisible Physical Memory|. Only then it is possible to use the settings according to Figure 4.4.57b. The Figure shows that the representation relates to ||Creation Mode|| where it is possible to create multiple RD, assign them a different font for the device, as [V:] in the example, and join them different names, of course, provided that the total area RD's do not exceed 2812 MB as in the example. In the example in Figure elected an RD, which occupies the entire available space PAE. If checked the created RAM disk (L1 action), it is a choice |Properties| execute modification of existing data indicated RD toward new window ||Property Mode|| as shown in Figure 4.4.57c. All these settings will become active when repeated the computer, as shown in Figure 4.4.58.

|
|
| Figure 4.4.58 RAM-Disc as device. |
How to use the created RAM disk? Imagination users will surely find different solutions. It will most likely be in the area to accommodate modifications under pagefile.sys Figure 4.4.22, with the difference that it will make adjustments to [V:] where this file separately for 2 GB, with the rest slated for directory [Temp-IE] that is the setting for IE (Options /Tools/-/Internet Options/-||General||-|Settings|) is used in the size of 200 MB for its temporary files, while the rest is used for small temporary files in directory [Temp] for program support where specified directory can be defined. Example of this is seen in the following Figure.
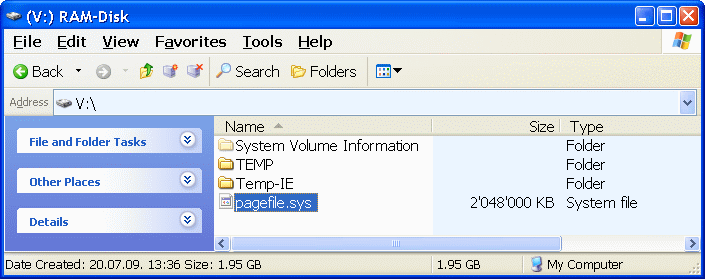 |
| Figure 4.4.59 Overview of selected content for the RAM-Disk. |
According to Figure 4.4.23 could put all the temporary files in the RAM-Disk. However, certain software, as 'WinRAR' when unpacking large facilities could be relatively small directory for temporary files of the RD sealed and prevent operation of the entire operating system. Therefore, it is better to define this space to a larger hard disk drive partition, and delete temporary files directory script of the example 4.4.2. Care must be taken off the computer power means the loss of all data on the RD, as the IE temporary files and virtual memory is not of importance. When rebooting the computer listed facilities will be renewed 'empty'. Ware system has another good characteristic. Selection ||Property Mod||-|Enable Image File| to select the file type .vdf in which to write computer shut down when the current contents of the RD and start your computer from it copied to the newly established blank RAM-Disk. Described is only part of the features of this effective program support, which can be downloaded here.
Processing of music and video content will be moved faster with the use of RD. RAM disk described in this example is only one of the possible ways of its use. The basic idea of which shows an example of the use of a much faster medium of physical disk for virtual memory system, thereby speeding in his work. Besides, dodge directory [Temp-IE] the RAM disk has a huge advantage. If you happen to 'harvest' a malicious program that can implant in this directory, shut down the computer simply disappears. Other Conditions? Users imagination is boundless. However users will likely exceed the 64 bit home / office operational systems to the software is gradually completing and designed just for them because this is the only way for the effective use of large memory resources.
SUMMARY:
Why does the general description of Windows applications, like Word, Excel ...? It is assumed that readers are approximate ECDL knowledge and all of the above is to extend the existing knowledge about the system. Moreover each of the newer versions of Microsoft operating systems 'pull' something from the past, and the relevant descriptions in the previous sections. For example, use two Windows Explorer (WE) windows is always the same and only the GUI is somewhat different, and the same should not be described in more places. Eventually there will be more of this e-book concepts connect couplings and will be easier to read it.
What we should pay attention to the reader is a system of policies, especially if he wants to monitor multiple networked computers, and 'Remote Cosole Access' is not even mentioned. Just in closing: Windows XP is available in two versions HOME and PROFESSIONAL. Has better resolved more detailed network settings, and the second one is common to the TWO courses of Microsoft operating systems merged into ONE, if you ignore the server component. And the servers? By GUI look like XP, but in the beginning, but is a huge difference, among them is the default everything is forbidden until the system administrator provides otherwise, the operating systems are 32-bit with effective PAE or 64 will have a lot more support for various services of web servers, e-mail to the database, and many other features that PC users have no work but are used by servers such as corporate anti-virus protection. Hardware difference is even more significant; motherboard with faster buses like PCI-X instead of PCI graphics card is usually integrated into the chipset (because it is of no importance), RAID server chip is a separate circuit with its own BIOS and memory, servers are not used non-ECC memory modules working as a computer user, microprocessors are more powerful and much more.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |