 Generally speaking, Figure 7.5.4 shows the basic physical topological structure of user connection to the Internet. Each of the displayed devices has its own software support (OS), which is usually written into the FLASH memory, and in principle they should have good signaling and a GUI interface (most often through a WEB-browser) for monitoring and adjusting the device's properties. It is not out of place for the person who maintains them to send warnings to his e-mail address in the event of some malfunction.The image shown refers to a business environment, and for home use or for small businesses (SOHO) one device unites all the devices shown up to the last level - the connection of the user's computer, or some other device such as a console player, and enables the user to connect to the Internet. Such a device is usually called a GATEWAY, and it is usually installed by the user's ISP (Internet Service Provider). The device combines several tasks and is therefore very complex, and there is a great variety in their performance. Setting up the connection with the ISP is done by the ISP and the user has no right of access to that part, while settings within the business or home environment are done by the user through some kind of graphical interface.
Generally speaking, Figure 7.5.4 shows the basic physical topological structure of user connection to the Internet. Each of the displayed devices has its own software support (OS), which is usually written into the FLASH memory, and in principle they should have good signaling and a GUI interface (most often through a WEB-browser) for monitoring and adjusting the device's properties. It is not out of place for the person who maintains them to send warnings to his e-mail address in the event of some malfunction.The image shown refers to a business environment, and for home use or for small businesses (SOHO) one device unites all the devices shown up to the last level - the connection of the user's computer, or some other device such as a console player, and enables the user to connect to the Internet. Such a device is usually called a GATEWAY, and it is usually installed by the user's ISP (Internet Service Provider). The device combines several tasks and is therefore very complex, and there is a great variety in their performance. Setting up the connection with the ISP is done by the ISP and the user has no right of access to that part, while settings within the business or home environment are done by the user through some kind of graphical interface.
The ISP is usually inclined to offer the user an older version of the device (such as the Thomson ST780) in order not to reduce costs, and usually uninformed users do not even know what current technologies offer. Currently, in the year 2022, the device should have these basic characteristics: Ethernet LAN connections (10/100/1000 mbps), Wi‑Fi 6E (minimum Wi‑Fi 6) wireless connections, WPA3 encryption standard, Sensors (DECT‑ULE, ZigBee, Z‑Wave) for IoT, NAS connection, 2.5 gigabit LAN and a malfunction report. Quality devices with the mentioned features are offered by brands such as Cisco, Asus, Linksys, TP-Link, Netgear (Orbi), AVM (FRITZ!Box) and perhaps some more, and everything else is some kind of ISP's 'magic' to get by as cheaply as possible, regardless of the fact that they brought the user back a decade. If there are too few Ethernet connections, their number can always be increased with an additional switch and thus provide the backbone of a small business-home network.
Wi‑Fi 6E is an extension of the Wi‑Fi 6 (802.11ax) wireless standard into the 6 GHz radio-frequency band (Figure 7.6.14). Wi‑Fi 6E builds on Wi‑Fi 6, which is the latest generation of the Wi‑Fi standard, but only Wi‑Fi 6E devices and applications can operate in the 6 GHz band. The following benefits of Wi‑Fi 6E stand out as the most important: Speed (bandwidth-intensive applications) and Security (Protected Access 3 - WPA3). This is essentially a huge technological leap in the understanding of business-home networking, as the need for Ethernet LAN ports becomes almost irrelevant. If you look at the devices and sensors that, for example, AVM offers for the Fritz!box (Figure 7.6.76), an efficient local network (Intranet) can be realized in a large spatial range, assuming that all devices use Wi‑Fi communication capabilities. Ethernet network infrastructure is taken over by Wi‑Fi 6E ( Wi‑Fi 7 ) and forms the wireless backbone of the local (home) network.
So, the key devices for connecting the local network to the Internet and fast data flow within the local network are:
- GATEWAY + Switch -
The GATEWAY is the most responsible device in terms of Internet access speed. It should support IPv6 because that protocol is faster than IPv4, although basically IPv6 contains (encapsulates) IPv4. If the data packets arrive faster, a message will be composed of them sooner when they are all collected. If you want to support quality multimedia communications, Internet access speeds of 1-10 Gbps are required. This does not mean that this speed will always be reached, because in some part of the Internet the signal may have to go through a slower router. Similar to a chain made up of anchors with different thicknesses; it all depends on the thinnest anchor. The switches within the network must match the speed of the router. Network cards with a communication speed of 2.5 Gbps are already a reality, and 10 Gbps switches will also become a normal reality. With new technologies, it is possible to achieve such high speeds via RJ45 connection and connection cables and equipment of category C7.
The implementation of this approach should be viewed according to the following:
- Big companies -
Large companies with a few hundred employees or more, with the use of numerous sensors, require many connections, which implies the implementation of IPv6 and 10 Gbps speed switches. This will enable, for example, video conferences and improve business.
- Small companies & SOHO -
Firms with a hundred or fewer employees will use the same principle as large firms, but a SOHO environment does not require such large resources. One device that will combine the functionality of a router and a switch (GATEWAY) is enough, which will have one 2.5 Gbps port for connecting to a computer and possible expansion with a 10 Gbps speed switch as the backbone of the network. In the SOHO environment, the MASH network realized by wire or wireless comes to the fore.
- Wireless Access Point -
Large and small companies will certainly use fast networks according to Wi‑Fi 6E ( Wi‑Fi 7 ) due to video conferences and sensors, while in a SOHO environment, a high-quality GATEWAY that can use a wireless network to achieve a MASH network topology will be sufficient.
At the Figure 3.6.26 are shown the ways in which the ISP connects SOHO users to the Internet. They all have in common that everything offered by the ISP is brought to the DSLAM (Digital subscriber line access multiplexer) device mainly by optical cable. The DSLAM device is set up to serve a city quarter, residential or family building or one floor in a residential building, and depending on the design, the GATEWAY can also be connected with an optical connection to the DSLAM. Basically, three services are offered:
- Internet -
A basic service that enables connecting to the Internet at different speeds according to the principle of 'what you pay is what you get', which also includes the user's private local network. It can be upgraded with/or Television and/or Telephone services.
- Television -
Program packages for watching TV programs and listening to music content in the scope of content according to the same principle as the previous item. According to this item, two application technologies are distinguished:
- Cable TV -
The QAM modulated signal is fed to two devices: GATEWAY and STB (Set Top Box) via a coaxial cable and splitter. The frequency range is divided into two areas (Figure 3.6.25b-III), one of which is used for receiving a modulated high-frequency TV signal, and the other for communication with the ISP regarding content selection. The frequency range used in this technology is very large, and without difficulty part of the channel is used for communication via the TCP-IP set of protocols to enable communication with the Internet. Due to the selection of TV program content, part of the channel uses TCP-IP communication, which is achieved through the GATEWAY, to which the STB is connected with an Ethernet cable. Communication is fast and stable. So, at first the transmission of an analog TV signal via cable, followed by evolution in terms of modulation with a digital TV signal and as a welcome possibility Internet connection.
- IP TV -
Originally, the PTT pair was used for the telephone (Figure 3.6.25b-a), but the advancement of technology allowed connection to the Internet with fast data transfer using the TCP-IP set of protocols (Figure 3.6.25b-c). Then, technological progress enabled sufficient speeds to reconstruct a digital TV signal by quickly assembling of TCP-IP packets. Now the quality of transmission of TV content is almost the same as that of cable television, provided that the DSLM device is as close as possible to the GATEWAY device.
- Telephone -
Mostly unlimited conversations with all fixed and mobile networks in the domain of the ISP. Now an incidental service in addition to the first two services listed.
By considering the explanation of the services offered by ISPs, it can be seen that the cable concept is superior, but it is profitable only in large cities. For remote locations, the solution is the IP-TV concept. The author of these lines is fortunate to be a user of the cable infrastructure, and therefore the continuation of the content of this page covers mostly that concept. The picture shown in the header of this page shows the menu that Fritz!box products usually have, in this case the cable GATEWAY FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable.In summary, the features of this device are:
- DOCSIS 3.1 for gigabit speeds over cable Internet.
- Wi-Fi 6 up to 2400 + 600 Mbit/s with MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) antenna technology.
- Telephone system, cordless telephony, Smart Home.
- For 6 cordless telephones, including answering machine. The integrated fax machine function and HD telephony complete the package.
- Network with 1 x 2.5 gigabit LAN, 4 x Ethernet 10/100/1000 Mbps LAN, 1 x USB 2.0.
- Media server service, NAS connectivity, MyFRITZ! service, OS auto update.
Thanks to Wi‑Fi 6 with Multi-User MIMO and a 2.5 gigabit LAN port, the FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable is a home networking hub at which can be relied on without fear. MIMO (multiple input, multiple output) is an antenna technology which use numerous small antennas to boost bandwidth to user based on a different setup called time division duplex (TDD). Like a multi-lane highway; joint operation of several transceiver devices. The new Wi‑Fi standard is designed to expertly supply multiple devices with Wi‑Fi, reliably and at top speeds. Supports Mesh Wi‑Fi, meaning your videos, music and photos seamlessly reach every corner of your home, apartment or office. Offers up to 6 Gbps downstream speed and is backward compatible with EuroDOCSIS 3.0. Fast Wi‑Fi 6 enables wireless internet access for all your multimedia devices, while Multi-User MIMO provides for top data transmission rates even when multiple devices are in use at the same time. Computers, laptops, game consoles, tablets and smartphones: the number of devices in the home with is growing all the time. To protect your communication and data from unauthorized access, the FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable features a sophisticated security concept. FRITZ!OS is the operating system of FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable device. By the browser-based interface can not only manage network and telephony functions, but also receive new features through free updates on a regular basis. But that's not all: use the practical FRITZ!Apps software to access your data with your smartphone from on the go or to make calls within the home network and more. Just like the updates, FRITZ!Apps software are free of charge.
- Overview
That is The Homepage of the user Interface. Here are notice about version of FRITZ!OS, overview of all FRITZ!Box 6660 Cable functions and the devices in home network. Here are important notifications for the secure and reliable operation of GATEWAY. At this page is nothing for a change, it is the only information page, but all links on the page lead to some other menu.
- Internet
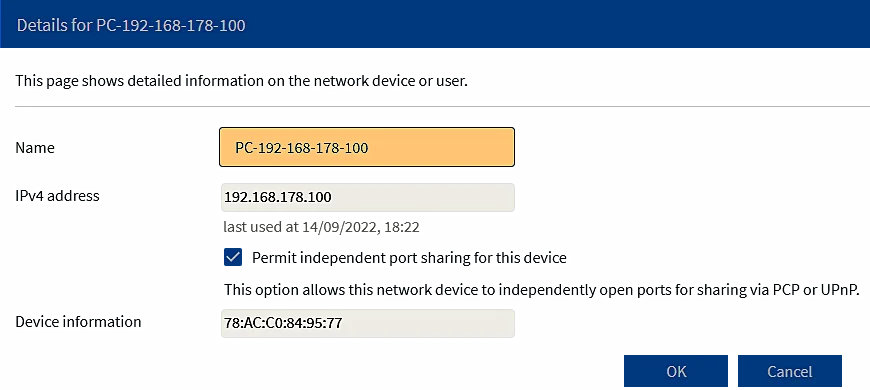
This menu with its sub-menus allows the user to see the operation of the device and some settings, which in principle do not need to be changed. But in the 'Type of Connection/AVM services/ option, the e-mail address of the user to whom the diagnostic data is sent can be added, and in the 'Permit Access/Port Sharing/Add Device for Sharing/ option, the IP or MAC address of the device in the network can be added which are available to everyone, such as a network printer.
 |
|
Figure 7.6.31 Adding the printer as an available device on the network.
|
If the printer knows how to use the device's DHCP service, it is not necessary to make it have a static IP address.
- Telephony
The data in this menu refers to the phone device, and nothing needs to be changed there unless the 'FRITZ' phone and its additional personal phones and sensors are used as shown in the picture 7.6.76.
- Home Network
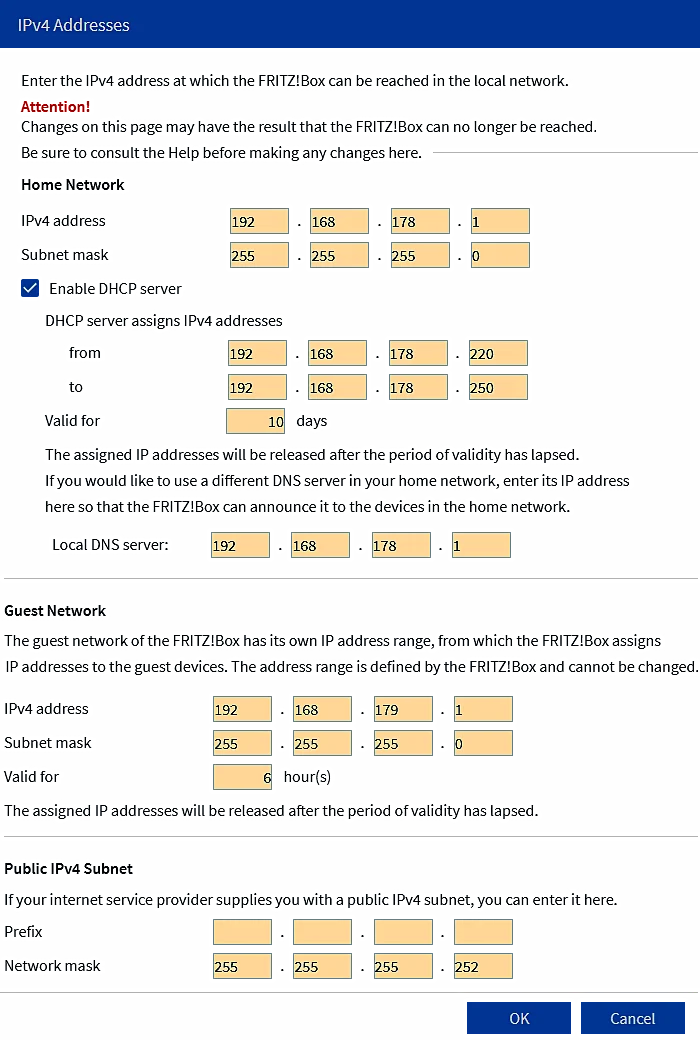
The 'Mesh' sub-menu has its role if additional FRITZ devices and sensors are used. Basically you don't need to touch anything because everything will connect automatically. But choice of 'Network' sub-menu and options '/Network settings/IP Addresses/IPv4 settings/' allows to made adjustments at network settings and the IP addresses used in the home network and guest network.
 |
|
Figure 7.6.32 Private IP addresses in the home network.
|
According to the Internet, the GATEWAY communicates with the IPv4 or IPv6 communication protocol, and within the local network, devices can communicate with each other using both of these protocols, but if there are a lot of older devices present, it is recommended to use IPv4 protocol, and the addressing of network devices is done according to the principles of the private ' C ' class, which provides additional security because the GATEWAY does not allow access to the private network from the Internet. Regarding older devices, compatibility of work from Wi‑Fi 3 to Wi‑Fi 7 is also required.
The 'USB / Storage' option will automatically recognize the USB drive when it is connected to the GATEWAY's USB port. But you have to be very careful. Since it is a USB v2.0 port (500 mA), you should choose a disk that consumes little power, such as 'WD_My-Passport', formatted as a FAT32 file system, and give it a suitable name. Otherwise, it will have to be messed with if another type of disc is used. In the instructions, there is no list of devices that are immediately recognized, although it is possible to use printers and some other USB devices.
The 'Media server' sub-choice should enable multimedia devices, including the USB drive that will be displayed. In the 'Fritz!box Name' sub-choice, the name GATEWAY is given to the device, which here is of course 'Buzdo'.
This GATEWAY has a built-in DNS service, which previous devices did not have. With the DHCP service, which 'holds' the range from the IP address 192.168.178.20 onwards without adjustment, the user has almost nothing to adjust. Turn on, connect and everything works. If the user wants to adjust something himself and prefers more static addresses, as shown in the example in the previous picture, he will reduce the range of IP addresses of the DHCP service, and give Wi-Fi networks different names as shown in the example below, and will enter his password and encryption type for the wireless network, add a user for the NAS and make a few more changes as he sees fit. DNS settings, as well as IP settings, must be entered in the network card (NIC) settings of the computer, or another device if necessary.
- Wi-Fi
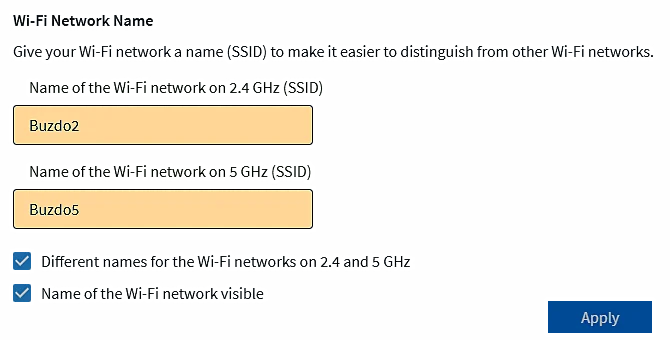
'Wi‑Fi Network/Wi-Fi Network Name' is the first sub-selection in this section where you have to enter the network name (SSID), and here the defaults are 'Buzdo2' and 'Buzdo5' (this device does not support frequencies of 6 GHz). In practice, it has been shown that it is good to specify that the frequency bands have different names and that it is not good to have a space in the name.
 |

|
|
Figure 7.6.33 Names of Wi-Fi networks.
|
|
It is still necessary to specify encryption in the 'Wi-Fi Network/security' option, and care should be taken to install an older system (WPA2 instead of WPA3) if there are older devices in the network.
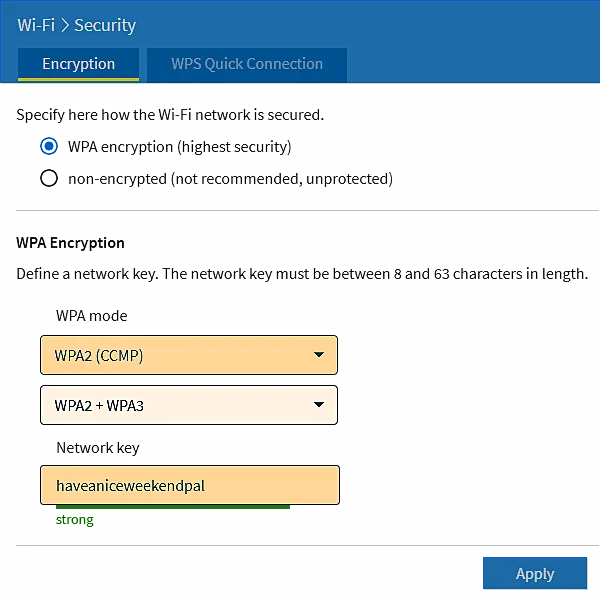 |

|
|
Figure 7.6.34 Security options.
|
|
The above are not the only security options. It will be possible to display most of the devices from the neighbors in the environment, and accordingly it can be updated whether that device is allowed to access the WiFi network or not. Wi‑Fi 6E ( Wi‑Fi 7 ) use a network 'token' for this purpose, which is unique to each GATEWAY.
- Smart Home
It is used only if additional devices are available.It is used only if additional devices are available.
- DVB-C
A very useful option that would be very worthwhile if the ISP does not normally deliver encrypted content. In that case, a couple of free music channels will appear in this list.
- Diagnostic
Diagnostic functions are available as marked in the FRITZ!Box settings. The results of the functional diagnostics can be saved. Also all FRITZ!Box settings relevant for security are listed and evaluated here. Any settings that may be insecure are indicated.
- System
The ability to view events during device operation, data on energy consumption, and the view shows you which push services are enabled in the FRITZ!Box. The option 'System/Fritz!Box Users' is of great importance because it is possible to add a user and specify what he is allowed to do on the device. The following is an example for NAS.
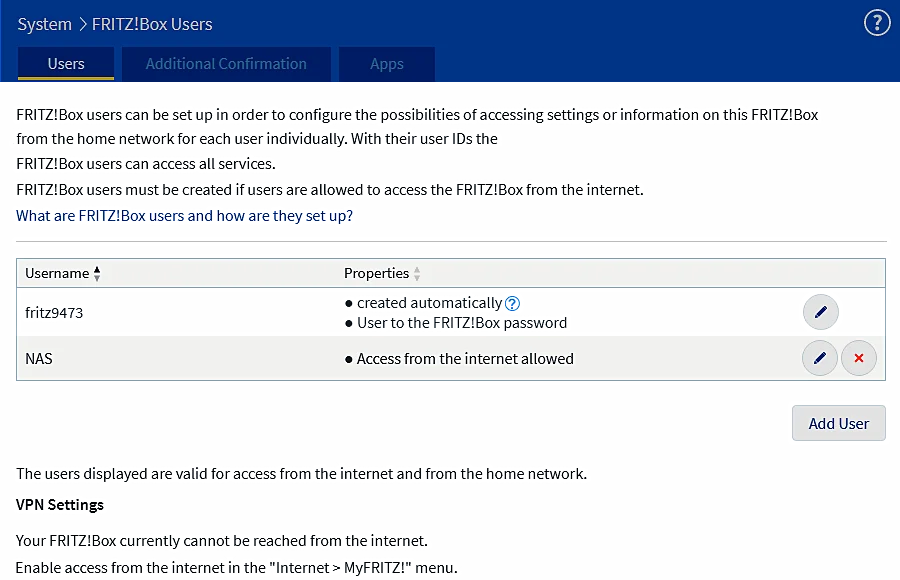
|
|
Figure* 7.6.35 NAS user and his rights.
( + / - )
|
A short and understandable name and a simple password should be chosen for the NAS, but with all restrictions except for the simple device access function.In addition, it is useful to map it as a disk device because the OS sees it as a directory.
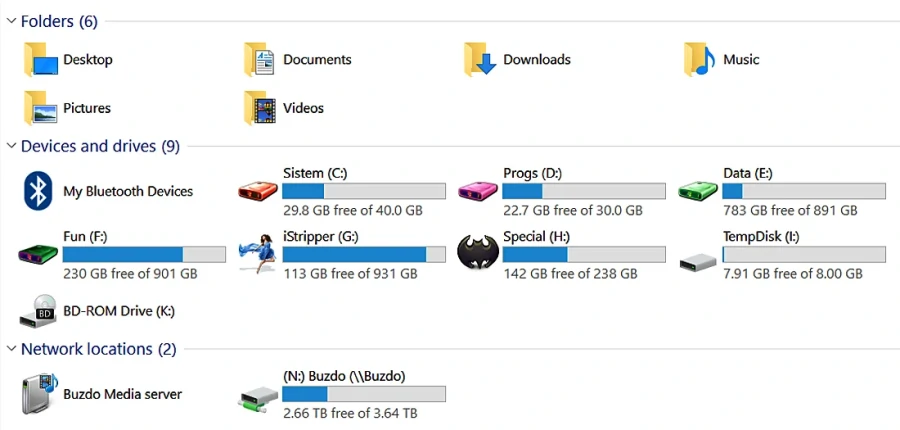 |
|
Figure 7.6.36 Mapped NAS drive at Windows OS.
|
A short and understandable name and password will allow easy access of all devices in the network to this directory.
- Wizards
Wizards that make it easy to set up your device.
Depending on the ISP, it is also possible to lease several STB devices, and if they are newer, they enable additional services, as shown in the following picture. One of the possibilities is to browse programs a few days back and watch them later, and it is also possible to record the desired program content in the ISP 'cloud', several movies for example, or mark some subsequent program content to receive a warning label. Then the specified program content is displayed in the 'My Library' selection and is saved for the user for a certain period of time.
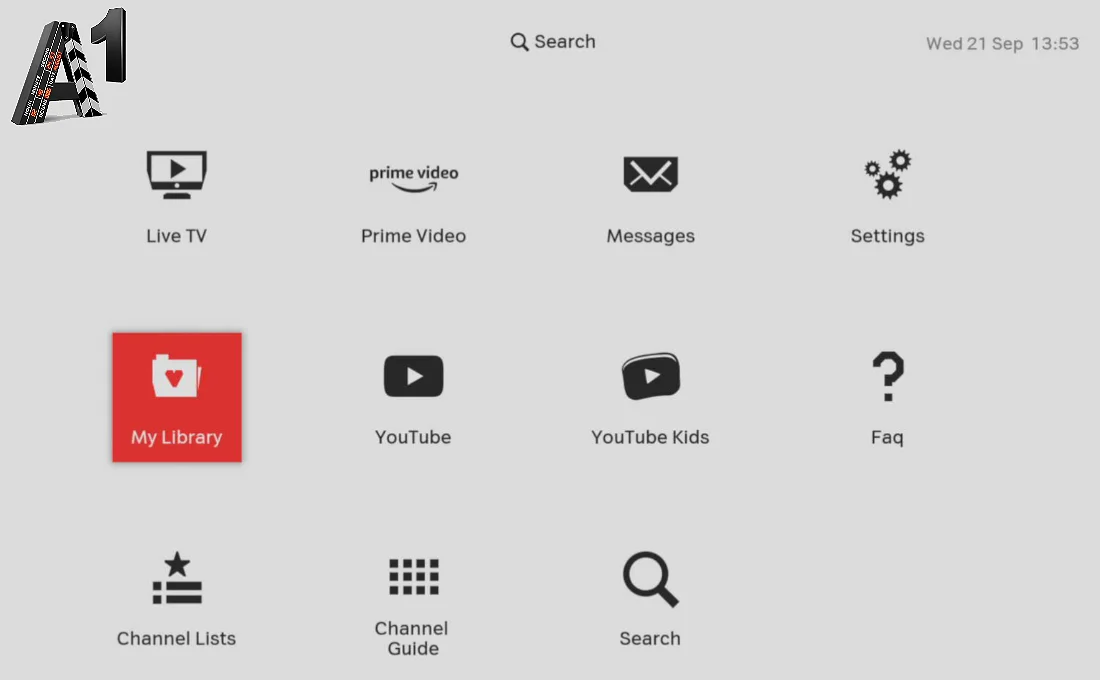
|
|
Figure 7.6.37 Advanced possibilities of using ISP services.
|
It's helpful if the STB has a disc recording port to plug into it. If this possibility does not exist, the new generation of devices for 'capturing' video content makes it possible. The following picture shows some of the devices for this purpose that are not too expensive. The basic principle of their operation is that the video signal is fed to the HDMI port and converted into a video signal readable via the USB 3.0 port. Even before, devices were made for this purpose, but due to the limitations of the USB 2.0 interface, they were not really usable. The USB 3.0 or later standard enables the transmission of video content in very high resolution. Of course, adequate software support is required, as the free software 'OBS Studio' which enables many things.

|
|
Figure 7.6.38 Devices for recording multimedia content on disc.
|
In doing so, care should be taken to ensure that the USB port can meet the energy requirements of these devices. USB ports on the motherboard usually cannot do this, and then the possibilities of the card shown in Figure 3.5.61 come into play. In the previous picture, the most expensive but also the most complete device is shown on the left. It has a port for external power, which eliminates the need for an energy-efficient USB card. The device has a microphone connection, which allows you to insert your own comments into the audio recording. Ideal if you want to create some kind of advertising content. The device shown in the middle of the picture works similarly to the one described above, but requires an energy-efficient USB port. The device shown on the far right is the simplest, it does not have an external power supply, HDMI signal transmission, or the ability to add audio tracks. All of them have in common a relatively high energy consumption and therefore heat up a little.
SUMMARY:
Everything described enables a different concept of connecting devices in the network compared to Figure 4.6.88, and the use of sensors to register the presence of gas, smoke (fire) and water (flooding) in an apartment or house. Very useful.
Citing of this page:
Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia.
{Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/file.
Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer
|
 Generally speaking, Figure 7.5.4 shows the basic physical topological structure of user connection to the Internet. Each of the displayed devices has its own software support (OS), which is usually written into the FLASH memory, and in principle they should have good signaling and a GUI interface (most often through a WEB-browser) for monitoring and adjusting the device's properties. It is not out of place for the person who maintains them to send warnings to his e-mail address in the event of some malfunction.The image shown refers to a business environment, and for home use or for small businesses (SOHO) one device unites all the devices shown up to the last level - the connection of the user's computer, or some other device such as a console player, and enables the user to connect to the Internet. Such a device is usually called a GATEWAY, and it is usually installed by the user's ISP (Internet Service Provider). The device combines several tasks and is therefore very complex, and there is a great variety in their performance. Setting up the connection with the ISP is done by the ISP and the user has no right of access to that part, while settings within the business or home environment are done by the user through some kind of graphical interface.
Generally speaking, Figure 7.5.4 shows the basic physical topological structure of user connection to the Internet. Each of the displayed devices has its own software support (OS), which is usually written into the FLASH memory, and in principle they should have good signaling and a GUI interface (most often through a WEB-browser) for monitoring and adjusting the device's properties. It is not out of place for the person who maintains them to send warnings to his e-mail address in the event of some malfunction.The image shown refers to a business environment, and for home use or for small businesses (SOHO) one device unites all the devices shown up to the last level - the connection of the user's computer, or some other device such as a console player, and enables the user to connect to the Internet. Such a device is usually called a GATEWAY, and it is usually installed by the user's ISP (Internet Service Provider). The device combines several tasks and is therefore very complex, and there is a great variety in their performance. Setting up the connection with the ISP is done by the ISP and the user has no right of access to that part, while settings within the business or home environment are done by the user through some kind of graphical interface.







