Microsoft Virtual PC 2007 |
The term virtual machine usually refers to a collection of separate computer units that separate communication technologies constitute the user the impression of working with one computer. By combining these computers creates a powerful 'virtual supercomputer', and the main task is to perform research charity (or military?) purposes. But if the user has a PC computer with sufficient processor, memory, graphics and disk resources on his computer can be a part of the operating system that is used to create one or more virtual machines with the same or some other operating system.
Basically, virtualization is enabling the operating system to a virtual machine through an intermediary - VIRTUALIZATOR, actual physical resources used computers and emulated computing resources offered virtualizator. It is done in two ways:
So, in the beginning only installed the operating system on the virtual machine, virtual machine behaves like a physical computer with a completely blank disk. Both ways virtualization hardware device supporting modern microprocessors which have incorporated an additional set of features (extensions) just for this purpose, the company AMD calls them 'AMD-V', while Intel its extensions named the 'VT-x'. It refers to a specific set of instructions for microprocessors.
In most cases, the an ordinary user at computer is used hosted virtualization, which means that the program support of virtualizator is primarily dedicated to work on an operating system (Windows, Linux, Mac OS X, Sun ...) in its 32 bit or 64 bit version, that is available in several versions. If user are using multiple operating systems simultaneously in examining and investigating individual, simulates network connectivity and the like, it is useful to the host computer has enough processing power and memory; multicore processors and 2 GB of RAM or more, for example, if the host computer with Windows XP operating system.
Viewership statistics of e-book 'Informatics Alphabet' shows that most visitors used Windows operating system (more than 90%). Therefore, it is described on this page free software 'Microsoft Virtual PC 2007' (no longer supports, but to the knowledge it was), primarily intended to host Windows operating systems and can be used, and commercial solutions that can host other operating systems like 'VMware', 'VirtualBox' or similar. Virtual PC basically requires no drivers to be installed in a virtual machine because it relies on the virtual PC emulation circuitry. The only computing devices which are used directly by a microprocessor and reserved space in RAM. The basic task of a virtual machine is to allow the execution of software in the operating system of a virtual machine that can not be executed in the operating system on the computer where it is installed Virtual PC, and since such a program support successfully used existing computer resources through Virtual PC service. Computing resources that serve Virtual PC must be powerful in order to be successfully served by virtualization (more powerful CPU, more RAM ...). Should have in mind that it is possible that the virtual machine can not reach all the advanced features of individual sets of computers, especially in games. Virtual PC is available as the extension of the Windows 7 operating system (XP Mode).
Another advantage is that the virtual machine can be used as needed to network more, and to analyze the different computer or network configuration, without affecting the contents of the computer where the virtual machines are installed. Indeed, ordinary copy protection (backup) files-disk virtual machine is possible, after some sort of failed experiments or analysis of a program of support, very fast virtual computer to restore the initial state. A new server or computer can be created by copying an file on existing drive, and by modifying a few parameters in the network configuration of new computer. Apart from this it is possible to use the network resources through a virtual computer on a separate physical computer that is more powerful, which means that the user does not necessarily have all the hardware and software components in its computer. Reminiscent of the client-server concept, which was once used by Novell, which is now among other things deals with virtualization, including among other things, allows you to have the same physical resources harnessed to work together 'Linux' and 'Windows' server. Thus, reducing the number of physical servers is one way to reduce equipment costs and simplify maintenance for unified environment.
After downloading the installation files and installation of software, the {Start} menu will appear the corresponding icon, and in the folder where it is installed will create a folder-directory-map [Virtual Machine Additions] that contains the following two files:
File type .ISO is image that contain the operating system files as the installation CD / DVD media, and it automatically launches the appropriate software required in the process of creating a virtual machine. When the 'Virtual PC' software (VPC) is activated support shows the initial working CONSOLE with menus as shown in Figure 1, but in which there is no icons of created computers. Choice /File/-/New Virtual Machine Wizard/, according to Figure 1b, offers the possibility of a method computers, and if it is chosen over the creation of new options |Create a virtual machine|, followed by the selection of the names of Virtual PC, which he describes .VMC file (Virtual Machine Configuration), the folder where to put his .VHD file (Virtual Hard disk), which is basically a computer disk which is dynamically resized to the virtual computer being used.

|
|
| Figure* 1. 'Virtual PC' console. ( + / - ) |
In the same way one can create .VFD file (Virtual Floppy Disk) that mimics the floppy device and can assign a virtual machine. Followed by selection of the Windows OS that wants to install and are available:
|
An interesting option |Add an existing virtual machine| which essentially means that they can be with another copy of the existing .VHD files and use ones already created and used computers. The preceding list does MS-DOS program support although under option |Other| can easily install. Followed by size selection of available RAM pointing to the fact that it is good to have a computer with as much physical RAM if it is to effectively use this program support (virtual memory of virtual machine in the associated him .VHD file), and then choose the location .VHD file name and its initial size. When all was done as described in the console icon appears of generated computer, and joins to the one .VHD file one .VMC file that connects devices to the virtual machine physically embedded devices, and contains the 'Microsoft Virtual Machine Options and Settings'. This file is an XML notation and can be restated in any text editor. Part of Windows 7.vmc file created during installation one Windows 7 operating system, with Windows VISTA initial setup is shown on.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?> |
File content changes each time you change the configuration during the startup and operation of the VPC. In view of the contents of one configuration files are extracted the data on a defined amount of RAM (512 MB), absolute and relative path through the tree file system to a virtual disk file 'Windows 7a.vhd' and 'Windows 7b.vhd' and directory on the physical hard drive [F:\00\] intended for the exchange of data between the host computer and the VPC, VPC by computer sees it as a network device [S:] in the descriptions onwards. Part of this configuration can be seen in the data in Figure 2 In the example described on this page physical disk directory [F:\00\] was used as a mapped network drive to exchange data and directory [F:\00\VPC\] as the directory in which they are located .vmc files and their associated .vhd files. Select a directory for each file is completely arbitrary will of the user. These examples are taken to comply with the descriptions that are discussed in other chapters of 'Informatics Alphabet'. As the basic configuration information found in the .vmc file, in the cases of copying VPC content to another computer, it is good that the destination computer has the same configuration as the original.
Using two virtual disks for VPC computer has the same rationale as for the use of two physical disk in a real computer, one to drive the operating system and the other for virtual memory, program support and facilities of temporary directories (temp), in accordance with the plan as shown in the installation table in Chapter 4.5. In both cases, accelerated work on the computer, whether it is a real computer or VPC computer.
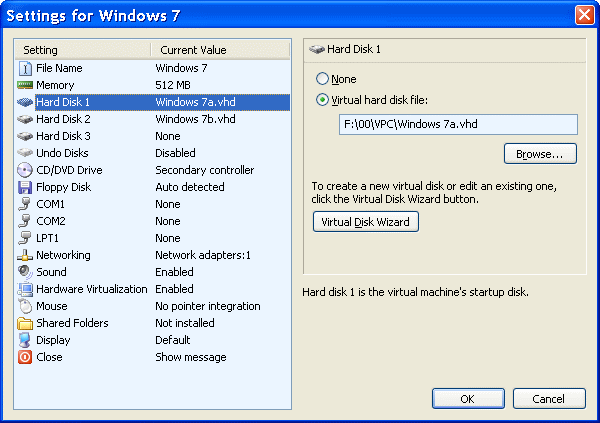
When all of this done, the virtual computer- VPC is created, but when the virtual machine starts following message that no operating system, which means that it needs to be INSTALL. Upon request to insert optical media should be inserted into the existing optical device corresponding optical media and perform installation of the operating system. After installing the operating system when you restart the virtual machine in the selection /Action/-/Settings/ get the virtual machine settings as shown in Figure 2a.
|
| Figure*** 2. Settings window of the virtual machine (VPC). ( + / - ) |
In Figure 2b, it can be established that in the current physical location of optical devices on the host computer selected letters [M:], [R:] and [W:], wherein [M:] refers to physically emulated optical disk on the host computer (software as 'Alcohol', 'Daemon' and the like) and other letters refer to physical optical devices on the host computer, where [R:] optical device a read-only medium, and [W:] an optical device for reading and writing. It should be emphasized that the optical devices that perform only the function of reading in general more precise and faster, and it may be good to use both types of device, especially if it is frequently used option to copy optical media. Letters depend on the manner in which the user has selected an optical device tag operating system on the host computer and the letters assigned to devices in VPC environment, for example, the letter [T:] (toaster) for optical device in the operating system at the VPC environment where the work assigned to one of these physical devices. Although devices can have the same label in both physical and virtual environments, this is not a good practice for ease of reference. Marking devices still need to plan.
The operating system can be installed from .ISO files if they are available on the disk on the host computer as indicated by the selection of Figure 2b, wherein the window provides a Windows Explorer to retrieve files. The Figure shows that with the call .ISO when the operating system already installed. Namely, that the installation process is fully completed this course should be VMAdditions.iso retrieve a file that contains the information necessary to retrieve the physical devices for the DOS operating system (such cdrom.sys or mouse.com), OS/2 and Windows operating systems. Besides the above this program support allows integration of the mouse between the real and virtual computers, time synchronization of clocks between computers, support for data exchange in a folder (shared folders), copy the text or images in a virtual computer and change the resolution of the window that displays a virtual computer, and its size on the desktop computer to the real standard values of 800×600, 1024×768 up to 1600×1200. After installing retrieved. ISO file through selection /Release CD/ should 'uncouple'. This means that you can call up any .ISO file to run or install some kind of software such as 'Microsoft Office' or some kind of game.
When you are making a new drive, in this case called 'Windows 7b.vhd', it should be added to the system selection |Virtual hard disk file:| and |Browse...| window choose already created a virtual disk file. Process of adding a virtual disk to VPC computer preceded its creation 'wizard' by choice /File/-/Virtual Disk Wizard/ as at Figure 1b. This is pure 'physical' action in which the Virtual PC environment creating a disc made as described in the VPC CONSOLE with 'power-off' VPC computer. When the virtual machine 'turns-on' Now you do not see the new virtual disk, although it is written in the corresponding .VMC file, but use operating system tools to assign virtual disks MBR records, determine its partitions and format them to make them available for the use of the operating system.
Virtual PC computer is completely independent computer, which requires regular updating it as far as patches, antivirus protection and a firewall, which assigns IP addresses to the network established by the scheme. If the virtual machine does not want to use the network's internal firewall (firewall) virtual machine is useful to stop all network traffic. Therefore, the virtual computer to watch like any other computer, and he regularly make the necessary updates and occasionally execute DEFRAGMENTATION. Defragmentation process and deleting individual files and folders can not be reduced sizes. VHD file. For this purpose, must be retrieved Virtual Disk Precompactor.iso file from the computer and launched by choice /CD/-/Capture ISO Image.../ (Figure 2b) and automatically runs a program precompact.exe which enter 'zero' of the deleted content and made preparation for compression .VHD files to a minimum. Of course, further work .VHD files will grow again, and the procedure needs to be repeated periodically.
Compression algorithm .VHD file, after previously preparing the file, execute the shutdown(turned-off) of virtual machine wizard and selecting the 'Virtual PC Console' (Figure 1) /File/-/Virtual Disk Wizard/ further steps in selection |Edit an existing virtual disk| and selection (button |Browse...|) belong .VHD file, and finally choosing |Compact it| and |Replasing the original File|, followed by the conclusion of the wizard compression algorithm.
Relationship with the environment regarding the exchange of data-files created from VPC COMPUTER by choice /Edit/-/Settings/-|Shared folders| where is selected already created folders in your PC that 'turned-on' virtual computer sees as a disk which is awarded one free letter of the alphabet. In the example in Figure 2c to the disc [S:]. This disc can be seen as a network drive and if the virtual machine wants to install some software must be copied from a network drive to a folder from the virtual drive and install from there. Over the network can be installed only developed that is designed to take advantage of network connectivity. In the manner described can be made available to multiple folders but each folder can only be awarded a letter that is not already used for the other device or an existing folder. Alongside these settings can be choosing /File/-/Options/ as at Figure 1b obtained by setting options are shown in Figure 2d.
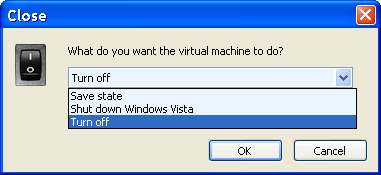
Although virtual machine exists in its own window, not good shutdown virtual computer by closing the window, but it must be done by regular selection /Action/-/Close.../ as at Figure 2b, and to open the window as shown in the next picture.
|
| Figure 3. Procedure 'shutdown' of Virtual PC. |
Should choose /Shut down .../ because otherwise when you restart the virtual machine are delineated as if the computer is shut down forcefully, as in Figure 4.4.6. Although virtual computer 'spins' in its own window, as shown in Figure 2b, it is a combination of keys <ALT Gr> + <Enter> (right <ALT> key) to switch to a 'Full-Screen Mode', and press the <ALT Gr> releases the mouse pointer of 'captivity' in the virtual machine window. Placing the mouse cursor on the virtual machine window and L1 action, shifts in the activity of the virtual computer mouse. Example of using Virtual PC is shown in Chapter 4.5 to install Windows 7 operating system, in Chapter 5.1 for installation 'Debian Linux' operating system and Chapter 5.2 to install 'Ubuntu Linux' operating system, related and unrelated operating system, the operating host system - Windows XP.
Virtual PC software (VPC) mimics-emulates a standard PC, and program support itself can be downloaded and used for 32 bit and 64 bit version. Imitate all key computer components other than microprocessors, namely:
From these characteristics, it is clear that virtualization is not characterized by strong support for graphics. This did not really matter because in essence, the purpose of virtualization is to exploit the strong computational power of clusters at the computer, or to enable work on some older computer programs on the user's computer. All virtual machines will have identical hardware structure. A problem may arise if the .vhd file has been transferred from a computer with an AMD microprocessor and its associated chipset on the Intel platform, because when you install the operating system on a computer requires the correct version of the core (kernel). This also means that you will be able to install any version of Linux that support PC-compatible boards, but will not be able to install the 'Apple Macintosh', i.e. its OS X operating system because the hardware completely different from the usual PC components.
There are commercial versions of software types VPC that it can be, but for the ordinary user described version is more than enough. Since it is a computer in the computer, the computer on which it is installed Virtual PC software called HOST, and computers that are the product of VPC called GUEST or Virtual Machine (VM). VPC is not known to imitate the image 24 bit color depth or higher which should be taken when installing the operating system.
These descriptions refer to the 'Virtual PC' version of software, which is free and has the full name of 'Microsoft Virtual PC 2007 SP1', version 6.0.192.0. It can be downloaded from Microsoft's sites in the version for 32 bit and 64 bit architecture. Her work is supported by the following operating systems: Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista and Windows XP SP2/SP3. Improvements in the form of supplements called 'Hotfix rollup package for Virtual PC 2007 Service Pack 1 - KB958162.msp' for 32 bit and 64 bit architecture delivers including support for operating resolutions up to 2048×1920 px (32b), and recognized as the building blocks VPC program support to version 6.0.210.0. This version should not be confused with the product 'Windows Virtual PC', which is a feature of Windows 7 operating system as a feature of the hatches of support for the reliable operation of Windows XP applications in Windows 7 environment, as well as with commercial server versions of this program support.
It has already been stated that in addition to described the software for the Windows platform, there are products from other manufacturers, such as 'Oracle (Sun) xVM VirtualBox' shown in Figure 5.8. How can it be possible that some of the products declare some computer resources as their own or their virtual resources so general that they are visible as physical resources, it is not recommended to have installed more products of this type of software from different vendors because of the possibility of their mutual interaction in the configuration program support, and disrupting their proper operation.
If virtualization is discussed in the context of a data center, the most important benefits of virtualization are reducing the need for large number of physical servers, rapid deployment of new servers, higher efficiency and flexibility of computing resources, increased server utilization and significantly lower costs. New technologies have enabled a very powerful hardware resources are independent might not fully utilized in terms of using one computer as a server, and to enable more efficient use of virtual machines within the same physical environment, it is no wonder that the virtual technology is rapidly evolving, and evolving mechanisms are using virtual networks within the same physical network infrastructure.
|
Citing of this page: Radic, Drago. " Informatics Alphabet " Split-Croatia. {Date of access}; https://informatics.buzdo.com/specific/file. Copyright © by Drago Radic. All rights reserved. | Disclaimer |